
Expertise: Crisis leadership, mission leadership, strategy, communications, web strategy, digital media, crisis recovery, public health, Northeast Asia, UN system.
Location: Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia 1997 to 1999
UN/UNDP Mongolia Communications Coordinator: David South
Click here to view images for this case study: CASE STUDY 4: UN + UNDP Mongolia | 1997 - 1999 Images
Abstract
“The transformation of Mongolia from a largely rural nomadic society of herdsmen to a community dominated by the increasingly ultra-globalized city of Ulan Bator, where almost a third of the population lives, is nothing short of astounding.” The New Mongolia: From Gold Rush to Climate Change, Association for Asian Studies, Volume 18:3 (Winter 2013): Central Asia
From 1997 to 1999, I served as the Communications Coordinator (head of communications) for the United Nations (UN)/United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) mission in Mongolia, founding and directing its UNDP Mongolia Communications Office.
About
The question posed itself from the start of the assignment: In the middle of a major crisis, is it possible to recover quickly while simultaneously growing and modernizing the United Nations mission (this was the dawn of the digital revolution)? It was only possible by teaching and mentoring colleagues, offering leadership, vision, strategy, and practical actions to get there - all with a budget and mandate for two years.
The mission had to tackle in particular, three, severe crises: the country's turbulent transition from Communism to free markets and democracy, the social and economic crash this caused, and, later in 1997, the Asian Financial Crisis (Pomfret 2000)* - all combined with the political instability this exacerbated. Richard Pomfret said in 1994, “In 1991 Mongolia suffered one of the biggest peacetime economic collapses ever (Mongolia’s Economic Reforms: Background, Content and Prospects, Richard Pomfret, University of Adelaide, 1994).” From Curbing Corruption in Asia: A Comparative Study of Six Countries by Jon S. T. Quah: "The combined effect of these three shocks was devastating as 'Mongolia suffered the most serious peacetime economic collapse any nation has faced during this century'. Indeed, Mongolia's economic collapse 'was possibly the greatest of all the (peaceful) formerly'" Communist countries.
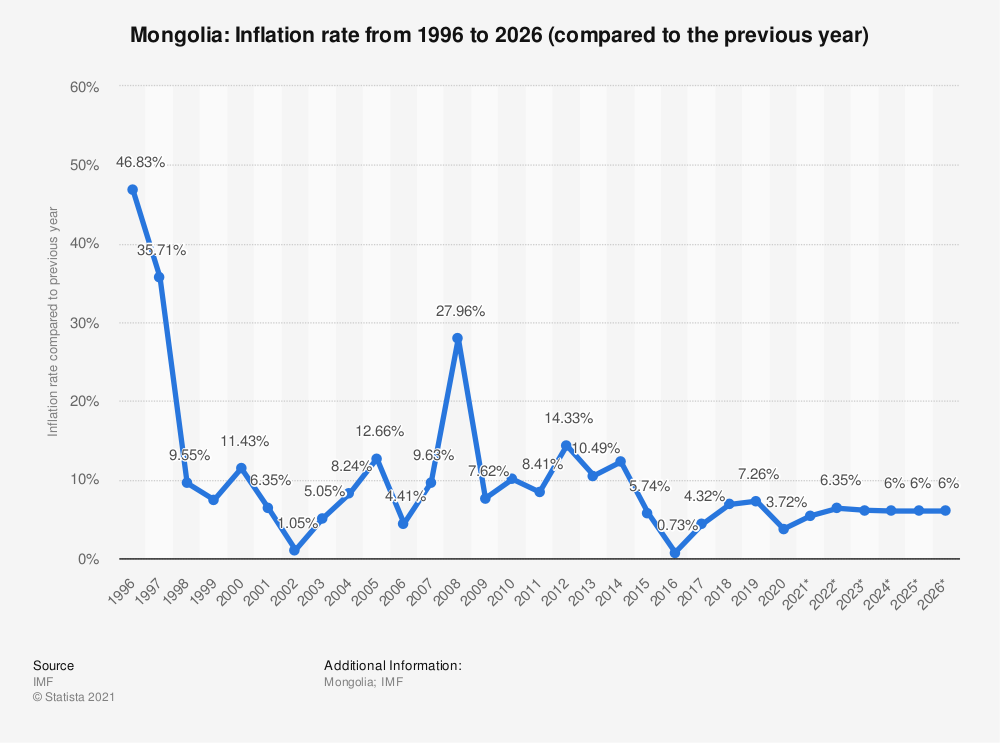 A dramatic decline in inflation paired with political and economic stabilisation allowed Mongolia to enjoy the fruits of the fast-growing economies of the 2000s. Source: Statista.
A dramatic decline in inflation paired with political and economic stabilisation allowed Mongolia to enjoy the fruits of the fast-growing economies of the 2000s. Source: Statista.
Find more statistics at Statista.
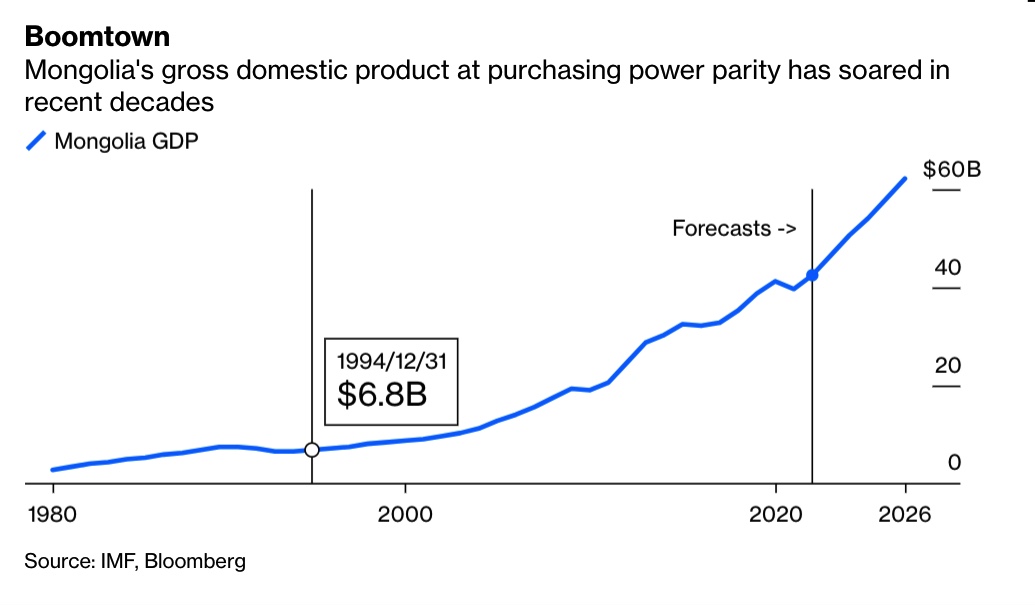 A resources “boomtown” throughout the 2000s. Source: Bloomberg. When I left in 1999, Mongolia’s PPP was US $8.8 bn; today (2021) it is US $42.4 bn.
A resources “boomtown” throughout the 2000s. Source: Bloomberg. When I left in 1999, Mongolia’s PPP was US $8.8 bn; today (2021) it is US $42.4 bn.
In this role, I pioneered innovative uses of the Internet and digital resources to communicate the UN's work and Mongolia's unfolding crises. The UN called this work a “role model” for the wider UN and country offices. A survey of United Nations country office websites in 2000 ranked the UN Mongolia website I launched in 1997 and oversaw for two years (1997-1999), third best in the world, saying: “A UN System site. A very nice, complete, professional site. Lots of information, easily accessible and well laid out. The information is comprehensive and up-to-date. This is a model of what a UNDP CO web site should be.” (http://www.scribd.com/doc/274319690/UNDP-Mongolia-United-Nations-2000-Survey-of-Country-Office-Websites)
“The years 1998 and 1999 have been volatile ones for Mongolia, with revolving door governments, the assassination of a minister, emerging corruption, a banking scandal, in-fighting within the ruling Democratic Coalition, frequent paralysis within the Parliament, and disputes over the Constitution. Economically, the period was unstable and rife with controversies.” Mongolia in 1998 and 1999: Past, Present, and Future at the New Millennium by Sheldon R. Severinghaus, Asian Survey, Vol. 40, No. 1, A Survey of Asia in 1999 (Jan. - Feb., 2000). pp. 130-139 (Publisher: University of California)
As part of a strategic plan to raise awareness of Mongolia’s development challenges and to spur action on meeting them, a Communications Office was established for the UN mission in 1997 - a structure that is commonplace in UN missions today. The Office also led on digital communications, marking many firsts, from the first digital photo and video library, the first online magazine, the first web portal, the first online newsletter, and many other firsts. It gathered numerous stories on resilience in a crisis, and documented in data and storytelling the country’s development challenges, while introducing a transparent way of working and communicating unprecedented for the time (the country was still recovering from the state secrecy of its years under Communism), and led on modernizing communications in the country. Acting as a strategic hub, the Communications Office and its dynamic and talented team, were able to leverage the existing budget to spur action on many fronts, including:
UN/UNDP Mongolia Development Web Portal (www.un-mongolia.mn)
I launched it in 1997 in the middle of a major crisis, and oversaw its expansion and development for two years. A pioneering digital resource, this award-winning United Nations Mongolia development web portal was singled out by UN headquarters in New York as an example of what a country office website should be like. It featured extensive resources in both Mongolian and English and also was home to the bilingual online magazine, Ger - Mongolia's first web magazine. It can be viewed at www.archive.org and there is more at Wikipedia here: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ger_(magazine).
Media
Working with journalists and media both within Mongolia and outside, the Communications Office was able to significantly raise awareness of Mongolia and its development challenges. This was reflected in a substantial increase in media coverage of the country and in the numerous books and other publications that emerged post-1997. The book In Their Own Words: Selected Writings by Journalists on Mongolia, 1997-1999 (ISBN 99929-5-043-9) published by UNDP Mongolia archived the stories by theme.
Ger Magazine
Ger Magazine (the Mongolian word for home and traditional tent dwelling) was published as the country’s first e-magazine in 1998. There were four issues in total from 1998 to 2000. The launch issue was on the theme of youth in the transition. Mongolia was transitioning from Communism to free markets and democracy and this had been both an exhilarating time and a wrenching time for young people. The magazine drew on talented journalists from Mongolia and the handful of international journalists based there to create a mix of content, from stories about life adapting to free markets to stories on various aspects of Mongolian culture and life.
The second issue of the magazine proved particularly effective and inspiring, with its modern life theme and cover story on a thriving Mongolian fashion scene.
Archived issues of the magazine can be found at the Wayback Machine here: https://archive.org/. Just type in the UN Mongolia website address for the years 1997 to 1999: www.un-mongolia.mn.
An online survey of the state of Mongolia’s media and its history (www.pressreference.com/Ma-No/Mongolia.html), had this to say: “An interesting variation from some of the other publications available is Ger Magazine (published online with guidance from the United Nations Development Program, UNDP), which is concerned with Mongolian youth in cultural transition. The name of the magazine is meant to be ironic because a ger is the Mongolian word for yurt—a yurt being traditional nomadic housing—but the magazine is about urbanization and globalization of Mongolian youth.”
Blue Sky Bulletin
The Blue Sky Bulletin newsletter was launched in 1997 initially as a simple, photocopied handout. It quickly founds its purpose and its audience, becoming a key way to communicate what was happening in the country and a crucial resource for the global development community, scholars, the media and anyone trying to figure out what was happening in a crazy and chaotic time. It eschewed the typical ‘grip and grin’ content found in many development newsletters and instead offered stories, data and insights useful to anyone seeking to understand Mongolia’s development challenges. The Blue Sky Bulletin was distributed via email and by post and proved to be a popular and oft-cited resource on the country. The quality of its production also paralleled Mongolia’s growing capacity to publish to international standards, as desktop publishing software became available and printers switched to modern print technologies. The Blue Sky Bulletin evolved from a rough, newsprint black and white publication to becoming a glossy, full-colour, bilingual newsletter distributed around Mongolia and the world.
Archived issues can be found online here:
Blue Sky Bulletin Issue 1
Blue Sky Bulletin Issue 2
Blue Sky Bulletin Issue 3
Blue Sky Bulletin Issue 4
Blue Sky Bulletin Issue 5
Blue Sky Bulletin Issue 6
Blue Sky Bulletin Issue 7
Blue Sky Bulletin Issue 8
Blue Sky Bulletin Issue 9
Blue Sky Bulletin Issue 10
Publishing
MHDR 1997
The Mongolian Human Development Report 1997 (MHDR), the country’s first, placed the story of the Mongolian people during the transition years (post-1989) at its heart, using photographs, stories and case studies to detail the bigger narrative at play.
This groundbreaking Mongolian Human Development Report – the country’s first – went beyond just chronicling Mongolia’s state of development in statistics and graphs. Designed, laid out and published in Mongolia, the report broke with the practices of many other international organisations, who would publish outside of Mongolia – denying local companies much-needed work and the opportunity to develop their skills. The report’s costs helped to kick-start a publishing boom in the country and significantly raised standards in design and layout in the Mongolia. The foundations laid down by the project producing the report ushered in a new age in publishing for Mongolia.
The report’s launch was innovative, not only being distributed for free across the country, but also part of a multimedia campaign including television programming, public posters, town hall meetings and a ‘roadshow’ featuring the report’s researchers and writers.
The initial print run of 10,000 copies was doubled as demand for the report increased. To the surprise of many, once hearing about the free report, herders would travel to the capital, Ulaanbaatar, to pick up their copy. The report proved people cared passionately about the development of their country and that development concepts are not to be the secret domain of ‘development practitioners’. The report also became an English language learning tool as readers compared the Mongolian and English-language versions.
You can read the report's pdf here: http://www.mn.undp.org/content/mongolia/en/home/library/National-Human-Development-Reports/Mongolia-Human-Development-Report-1997.html
Mongolian AIDS Bulletin
UNDP acted swiftly to address a breaking HIV/AIDS crisis in 1997, offering a key lesson for others working in public health (the Ebola Crisis and global air pollution crisis both show those lessons have still yet to be fully absorbed).
Assembled by a team of health experts after the Fourth International Congress on AIDS in Asia and the Pacific, the Mongolian AIDS Bulletin was published in 1997 in the middle of an HIV/AIDS crisis. It provided timely information and health resources in the Mongolian language and was distributed across the country.
“Mongolia’s first AIDS Bulletin marked the beginning of the UNDP Response to HIV/AIDS/STDs Project back in the autumn of 1997. Over 5,000 copies of the magazine were distributed across the country, offering accurate information on the HIV/AIDS situation. The project has been pivotal in the formulation of a national information, education and communication (IEC) strategy, bringing together NGOs, donors, UN agencies and the government.”
Source: YouandAids: The HIV/AIDS Portal for Asia Pacific
Green Book
In the Mongolian language, the Mongolian Green Book details effective ways to live in harmony with the environment while achieving development goals. Based on three years' work in Mongolia - a Northeast Asian nation coping with desertification, mining, and climate change - the book presents tested strategies.
EPAP Handbook
The Environmental Public Awareness Handbook was published in 1999 and features the case studies and lessons learned by UNDP's Mongolian Environmental Public Awareness Programme (EPAP). The handbook draws on the close to 100 small environmental projects the Programme oversaw during a two-year period. These projects stretched across Mongolia, and operated in a time of great upheaval and social, economic and environmental distress. The handbook is intended for training purposes and the practice of public participation in environmental protection.
In its 2007 Needs Assessment, the Government of Mongolia found the EPAP projects "had a wide impact on limiting many environmental problems. Successful projects such as the Dutch/UNDP funded Environmental Awareness Project (EPAP), which was actually a multitude of small pilot projects (most costing less than $5,000 each) which taught local populations easily and efficiently different ways of living and working that are low-impact on the environment.”
Mongolia Updates 1997, 1998, 1999
Mongolia Update 1998 detailed how the country was coping with its hyperinflation and the Asian economic crisis.
The mission simultaneously had to deal with the 1997 Asian Crisis (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/1997_Asian_Financial_Crisis) and the worst peacetime economic collapse in post-WWII history (http://www.jstor.org/pss/153756).
Mongolia Update 1998 - Political Changes
1998 proved a tumultuous year for Mongolia. The country's existing economic crisis caused by the transition from Communism to free markets was made worse by the wider Asian Crisis. The government was destabilised, leading to an often-confusing revolving door of political figures. In order to help readers better understand the political changes in the country, a special edition of Mongolia Update was published that year.
UNDP Mongolia: The Guide
The Guide, first published in 1997, provided a rolling update on UNDP's programmes and projects in Mongolia during a turbulent time (1997-1999). The mission simultaneously had to deal with the 1997 Asian Crisis (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/1997_Asian_financial_crisis) and the worst peacetime economic collapse in post-WWII history.
Each edition came with short project and context summaries, key staff contacts, and facts and figures on how the country was changing. For the first time, any member of the public could grasp what the UN was up to in the country and be able to contact the project staff. An unusual level of transparency at the time for a UN mission.
Memoranda of Understanding
Three Memoranda of Understanding were negotiated with the Mongolian Government to help focus efforts and aid the attainment of internationally-agreed resolutions. This was affirmed by a series of youth conferences, One World, held in 1998 and 1999.
Strategy and Leadership in a Crisis
The scale and gravity of the crisis that struck Mongolia in the early 1990s was only slowly shaken off by the late 1990s. The economic and social crisis brought on by the collapse of Communism and the ending of subsidies and supports from the Soviet Union, led to a sharp rise in job losses, poverty, hunger, and family and community breakdowns.
The challenge was to find inspiring ways out of the crisis, while building confidence and hope. The sort of challenges confronted by the UNDP Mongolia Communications Office included:
1) A food crisis: agricultural production was down sharply, and the traditional nomadic herding economy, while at peak herd, was failing to get the meat to markets and to a high enough standard to restore export levels to where they once were. As a result, a cross-border trading frenzy became the solution to falling domestic food production and availability.
2) HIV/AIDS/STDs crisis.
3) A major banking crisis.
4) Both the Asian Financial Crisis and the Russia Crisis.
5) An ongoing political crisis and an inability to form stable governments.
UN Annual Reports
Editor and designer. 1998 Report called by Under-Secretary-General Nafis Sadik “a clear, well-written, attractive and colourful report.”
Timeline
1997: Arrive in the capital of Mongolia, Ulaanbaatar, to undertake a two-year assignment with the United Nations mission. Quickly get to work founding the UNDP Mongolia Communications Office and pursuing a strategic communications approach with a busy online and offline bilingual publishing programme. Launch award-winning UN Mongolia Development Web Portal (www.un-mongolia.mn). Launch first Human Development Report Mongolia 1997, and a Mongolian AIDS Bulletin during crisis. Assist the Government of Canada to establish the first Honorary Consul in Ulaanbaatar on December 1, 1997 and the Canada Fund Mongolia.
 Canada Fund Mongolia
Canada Fund Mongolia
1998: International media tours of the country, launching of Mongolia’s first online magazine, Ger, distribute globally a regular newsletter on Mongolia’s development challenges, Blue Sky Bulletin. Open United Nations Info Shop for the public. Assist the Government of Canada to connect with Canadians working with the United Nations in Mongolia during the first official visit by a Canadian Government Minister.
1999: Launch a string of books documenting insights gleaned from the Mongolia development experience.
Testimonials
“Mongolia is not an easy country to live in and David [South] showed a keen ability to adapt in difficult circumstances. He was sensitive to the local habits and cultures and was highly respected by his Mongolian colleagues. … David’s journalism background served him well in his position as Director of the Communications Unit. … A major accomplishment … was the establishment of the UNDP web site. He had the artistic flare, solid writing talent and organizational skills that made this a success. … we greatly appreciated the talents and contributions of David South to the work of UNDP in Mongolia.” Douglas Gardner, UN Resident Coordinator and UNDP Resident Representative Mongolia
Impact
Micro
- strategic communications approach including establishing the UN/UNDP Mongolia Communications Office and team and strategic communications plan
- led on digital transformation, including use of digitial media (photo/video archive) and digital publishing (web site, online magazine and newsletter, etc.)
- established and ran the United Nations Info Shop - a one-stop resource open to the public with archive of development publications and current periodicals and Internet access
- began largest bilingual online and offline publishing programme in country - led on publishing and design modernisation
- laid down the foundations for many UN initiatives in Mongolia that are still underway. Contributed to stabilizing the country in a turbulent time. Mongolia was briefly the fastest-growing economy in the world by 2011
- championed transparency and access to information and media freedoms
- oversaw a period in which Transparency International found lower levels of perceived corruption
- managing editor for country’s first Human Development Report
Macro
- raised profile of country and its development challenges. Donor pledges rose
- 2 international media tours
- strong relationship with Mongolian and international journalists
- championed innovators in commnications
- crisis response: AIDS, economy, political
- country’s largest website and one of its first. Called “Godfather of the Mongolian web”
- called a “role model” for the wider UN
- led on new approach to UN communications in the digital age
- design-led approach
- transparent and timely updates
- negotiated three Memoranda of Understanding (MOUs): youth, food security and nutrition, STDs/HIV/AIDS
- One World youth conferences
Publications
David South Consulting Summary of Impact
Environmental Public Awareness Handbook: Case Studies and Lessons Learned in Mongolia
Ger Magazine: Modern Life Issue
Ger Magazine: Youth Issue
Human Development Report Mongolia 1997
Mongolian Green Book
Mongolia Update - Coverage of 1998 Political Changes
Mongolia Update 1998
Mongolian AIDS Bulletin
Mongolian Rock and Pop Book
Partnership for Progress: The United Nations Development Programme in Mongolia
UNDP Mongolia Online Development Portal
UNDP in Mongolia: The Guide
Stories
Freedom of Expression: Introducing Investigative Journalism to Local Media in Mongolia
Lamas Against AIDS
Philippine Conference Tackles Asia’s AIDS Crisis
Starting from Scratch: The Challenge of Transition
UNDP Mongolia Partnership for Progress 1997 to 1999 Key Documents
A UNDP Success Story: Grassroots Environmental Campaign Mobilizes Thousands in Mongolia
Citations
The response by the UNDP Mongolia Communications Office has been cited in numerous articles, books, publications and stories. It has also contributed to the development of the human development concept and understanding of human resilience in a crisis and innovation in a crisis.
Book citations include:
Dateline Mongolia: An American Journalist in Nomad's Land by Michael Kohn, RDR Books, 2006
Modern Mongolia: From Khans to Commissars to Capitalists by Morris Rossabi, University of California Press, 2005
Wild East: Travels in the New Mongolia by Jill Lawless, ECW Press, 2000
Paper citations include:
Paula L. W. Sabloff (2020) Buying into capitalism: Mongolians’ changing perceptions of capitalism in the transition years, Central Asian Survey, 39:4, 556-577, DOI: 10.1080/02634937.2020.1823819
A more detailed list of citations can be found here:http://www.davidsouthconsulting.com/about/
For research purposes, key documents were compiled together and published online here: https://books.google.ca/books?id=K76jBgAAQBAJ&dq=undp+mongolia+key+documents&source=gbs_navlinks_s
This resource was praised for having: “Very useful references and original materials that documented UNDP Mongolia work. I needed to trace community-based development, and this book provided a valuable source.” Review on Google Books
In 2001, the UN won the Nobel Peace Prize for “their work for a better organized and more peaceful world” and its communications innovations, with work such as that in Mongolia being cited as a contributing factor to the awarding of the Prize.
In 2000, the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were launched in a 15-year bid to use a focused approach to development centred around eight goals to accelerate improvements to human development. From 2000 to 2005, consulting work was undertaken in various UN missions (Mongolia, South Africa, Turkmenistan, Ukraine) to communicate the goals and to reshape communications activities around the goals.
* Transition and Democracy in Mongolia by Richard Pomfret, Europe-Asia Studies, Vol. 52, No. 1 (Jan., 2000), pp. 149-160, published by Taylor & Francis, Ltd. (http://www.jstor.org/stable/153756?seq=1#page_scan_tab_contents)
The Milk of Kindness flows in a Peculiar Land A Steppe From Nowhere by Leslie Chang, The Asian Wall Street Journal, 15 August 1998
Mongolia prepares for a magazine explosion by Jill Lawless, UB Post, 08-09-98
Other Resources
Letter from Mongolia: Herding instinct by Jill Lawless, The Guardian, 9 June 1999


ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052
© David South Consulting 2017

 Whilst with a UK-based international development consultancy, I worked on the drafting and online launch in 2000 of the World Bank’s Task Force on Higher Education and Society report, Higher Education in Developing Countries: Peril and Promise. At the time, it was still rare to see report’s made user friendly for the world’s web audience. As a survey in 2014 discovered, a shocking third of the Bank’s publications are never downloaded, 40 per cent were downloaded just 100 times, and only 13 per cent were downloaded more than 250 times in their lifetime (The Washington Post).
Whilst with a UK-based international development consultancy, I worked on the drafting and online launch in 2000 of the World Bank’s Task Force on Higher Education and Society report, Higher Education in Developing Countries: Peril and Promise. At the time, it was still rare to see report’s made user friendly for the world’s web audience. As a survey in 2014 discovered, a shocking third of the Bank’s publications are never downloaded, 40 per cent were downloaded just 100 times, and only 13 per cent were downloaded more than 250 times in their lifetime (The Washington Post). Higher Education in Developing Countries: Peril and Promise (ISBN-0-8213-4630-X) website for the World Bank Task Force on Higher Education and Society. The Task Force's report, Higher Education and Developing Countries: Peril and Promise, was launched on March 1st 2000 at the World Bank in Washington.
Higher Education in Developing Countries: Peril and Promise (ISBN-0-8213-4630-X) website for the World Bank Task Force on Higher Education and Society. The Task Force's report, Higher Education and Developing Countries: Peril and Promise, was launched on March 1st 2000 at the World Bank in Washington.













