Editor: David South
Researcher and Writer: Jill Lawless
Publisher: UNDP Mongolia Communications Office
Published: Between 1997 and 1999
Background: This is the original text from the brochure UNDP in Mongolia: The Guide first published in 1997. It, for the first time, provided a rolling update on what the United Nations was doing in Mongolia, offering key contacts and data to help advance human development in the country. It introduced transparency to the UN's work in the country and made it easier to hold programme and project staff to account.
Mongolia - Population
With an area of more than 1.5 million square kilometres and a population of 2.38 million as of October 1997, Mongolia has a population density of only 1.5 people per square kilometre, one of the lowest in the world. The country has a relatively low growth rate of 1.6 per cent (1995), down from 2.5 per cent in 1989. At this rate, Mongolia's population will reach 2.5 million by the year 2000.
Despite the popular image of Mongolians as nomadic herders, it is an increasingly urbanized country - 51.9 per cent of the population is urban, 48.1 per cent rural. More than one quarter of Mongolians live in the capital city, Ulaanbaatar. The other major urban centres are Darhan (pop. 90,000) and Erdenet (pop. 65,000 ).
The country is divided into 21 aimags (provinces), plus the autonomous capital region. The aimags are:
In the centre: Tuv, Uvurhangai, Arhangai
In the north: Bulgan, Selenge, Hovsgul, Zavhan, Darhan-Uul, Orhon
In the east: Hentii, Dornod, Suhbaatar
In the west: Hovd, Uvs, Bayan-Olgii, Gov-Altai
In the south: Dundgov, Dornogov, Omnogov, Bayanhongor, Gobisumber
The People:
About 86 per cent of the country's population are Kalkh Mongols. Another 7 per cent are Turkic in origin, mostly Kazakhs living in the western aimags of Bayan-Olgii and Hovd. The rest belong to a wide variety of ethnic groups, including the Buryat, Dariganga, Bayad, Zakchin and Uriankhai. Mongolia's smallest ethnic group is the Tsaatan, about 200 of whom live as reindeer herders in the far north of the country.
During the communist period, Mongolia was home to tens of thousands of Russians. Few remain.
More than 4 million Mongols live outside Mongolia, in Russia and the Chinese province of Inner Mongolia.
Human Development:
- Mongolia's per capita GDP is U.S. $359 (1995). But this fails to take into account the cashless subsistence and barter economy widespread in rural areas.
- Poverty, though widespread, is difficult to tabulate. 1996 government figures put the poverty rate at 19.2 per cent - 19.8 per cent for rural areas, 18.7 for urban areas. But State Statistical Office figures for October 1997 indicate 36.8 per cent of urban residents and 27.5 per cent of rural Mongolians live below the poverty line.
- Omnogov, Gobisumber, Hovsgol, Ovorhangai and Bayanhongor are the aimags with the highest poverty rates.
- The average monthly household income in September 1997 was 58,516.7 tugrugs (U.S. $73). Average expenditure was 58,124.8 tugrugs. In 1995, 48 per cent of household expenditure went on food. In poor households, the figure was 64 per cent.
Social Data:
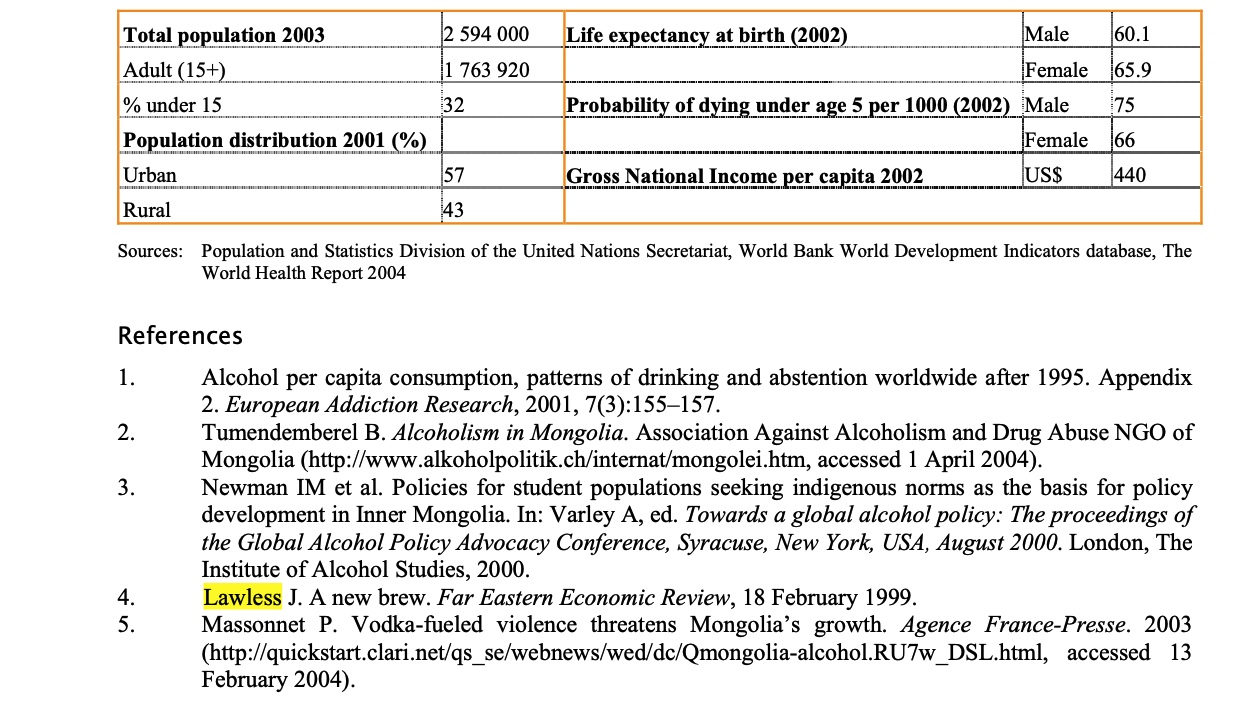
Life expectancy: 63.8 years (1995)
Infant mortality rate: 40 per 1000
Under five mortality rate: 56.4 per 1000
Maternal mortality rate: 185.2 per 100,000 (1995)
One-year-old immunization rate: tuberculosis 94.4 per cent, measles 85.2 per cent (1995)
Access to safe drinking water: rural 89.9 per cent, urban 46.1 per cent (1995)
Access to sanitation: 74 per cent (1995)
Adult literacy rate:
men 97.5 per cent,
women 96.3 per cent
Primary school net enrollment: 93.4 per cent
Secondary school net enrollment: 56.9 per cent
Physicians: 26 per 10,000
Hospital beds: 9.9 per 1000
Daily calorie intake: 2278.2
Data 1996 unless otherwise indicated. Sources: State Statistical Office, Human Development Report Mongolia 1997
Mongolia - Economy
An Economy in Transition:
After 70 years of centrally planned economy, Mongolia is embracing free-market principles with a vengeance. Economic liberalization began under the Mongolian People's Revolutionary Party government in the early 1990s. The Democratic Coalition government, elected in June 1996, has vowed sweeping economic changes, including privatization of state assets, liberalization of trade and promotion of foreign investment.
The foreign investment law now encourages foreign investment in the form of share purchases, joint ventures and wholly foreign-owned concerns. Mining companies are given significant tax holidays. In May, 1997 parliament abolished customs duties expect on alcohol, tobacco and oil products.
All of this has been a shock to Mongolia and Mongolians. The country's GDP shrank by a third in the early 1990s, though it has slowly recovered since. Inflation topped 300 per cent in 1993, but was brought down to below 50 per cent by 1997. The tugrug fell from 40 to U.S. $1 in 1991 to 800 to the dollar in 1997. Unemployment officially stands at 6.5 per cent - unofficial estimates are much higher.
The government's ambitious privatization scheme has stalled; manufacturing and exports are down; imports are up. Adding to the problems is the fact that world prices for Mongolia's major export items - copper and cashmere - have fallen.
The state retains at least 50 per cent ownership of the nation's flagship enterprises, including the national airline, MIAT, the Gobi cashmere company and the power stations.
Mongolia has a resource-based economy, exporting mostly raw materials and importing mostly processed goods. The top exports are mineral products, textiles, base minerals, hides, skins and furs and animals and animal products. The major imports include petroleum products, industrial equipment and consumer goods.
Mongolia's major trading partners are its two neighbours, China and Russia, though Korea and Japan are becoming more important - and the number-one export destination is Switzerland.
Sidebar: The rural economy
Half of Mongolia's population is rural, and herding remains the backbone of the Mongolian economy. Agriculture accounts for 30 per cent of the nation's GDP. The number of herding households grew during the economic turmoil of the early 1990s, and now stands at more than 170,000; there are 30 million head of livestock in Mongolia. Herders produce meat, skins and furs; more and more herders are investing in cashmere goats, a substantial money-earner.
Cultivation of crops, on the other hand, is limited. Before 1990, Mongolia was self-sufficient in cereals and even exported to the Soviet Union. But the sector suffered badly in the early 1990s. The 1997 harvest was 239,000 tonnes, 56 per cent of 1991-95 levels and only 40 per cent of pre-1990 harvests. Mongolia must now import 40 per cent of its cereal needs, a factor that contributes to a vulnerable food-security situation. Cultivation of vegetables is up, but remains minor - only 31,000 tonnes in 1997.
Sidebar: Rich in resources
Mongolia is resource-rich. This vast territory contains 15 per cent of the world's supply of fluorspar and significant deposits of copper, molybdenum, iron, phosphates, tin, nickel, zinc, tungsten and gold, as well as at least 100 billion tonnes of coal.
Copper is the nation's number one export.
Minerals account for more than a third of Mongolia's GDP and earn half of its hard currency. Gold production is increasing.
Mongolia also contains significant reserves of oil, which could transform the economy. But infrastructure and transportation limitations mean that commercial extraction is limited. The completion of a pipeline to China could change all this.
Economic Data:
Exchange rate: $1 = Tg 808 (Nov 1997)
GDP: Tg 185.5 billion (1996)
GDP per capita: Tg 228,605 (1996)
Inflation: 325 per cent (1992), 53 per cent (1996)
State budget expenditure: Tg 203.6 billion (Jan-Oct 1997)
State budget revenue: Tg 176 billion (Jan-Oct 1997)
Foreign aid (1991-97): U.S. 478 million
Official external debt: Tg 522 billion (Oct 97)
Industrial output: Tg 270.6 billion (Jan-Oct 97)
Exports: $334.2 million (Jan-Oct 97)
Imports: $343.3 million (Jan-Oct 97)
Workforce: employed: 791,800, unemployed 65,700 (Oct 97)
Source: State Statistical Office
Mongolia - Politics
Seven decades of communist rule in Mongolia began to crumble in 1990, when the collapse of the old Eastern Bloc brought the first pro-democracy demonstrations. The ruling Mongolian People's Revolutionary Party, which had already initiated a Mongolian version of glasnost, permitted the nation's first multiparty elections in July, 1990.
Superior organization helped the MPRP win both the 1990 and 1992 elections (taking 71 of 76 parliamentary seats in the latter), but reform picked up speed. In 1992, the country adopted a new Constitution that enshrined human rights, private ownership and a state structure based on separation of power between legislative and judicial branches.
In the June 1996 election, major opposition groups united to form the Democratic Coalition, made up of the National Democratic Party, the Social Democratic Party, the Believers' Party and the Green Party. Somewhat to its own surprise, the Coalition won a healthy 50 of 76 seats in the State Ikh Hural, or parliament. The composition of the Hural is now: National Democrats 35, Social Democrats 15, MPRP 25, Mongolian Traditional United Party 1.
In addition to their economic reforms, the Democrats have carried out radical restructuring of government, slashing the number of Ministries from 14 to 9.
The government has a healthy majority, but tensions sometimes emerge between the coalition partners. Mongolia's transition to democracy has been remarkably peaceful, and the young democracy is robust - there are now more than 20 political parties in the country.
But economic hardship has caused resentments. In the 1997 Presidential election, voters elected N. Bagabandi, the candidate of the MPRP. In the fall of 1997, the government had to face demonstrations from students and pensioners and an opposition campaign that led to a confidence vote in parliament -- a vote the government easily survived.
Political structure:
Mongolia has a parliamentary system of government, with a 76-seat legislature called the State Ikh Hural. The President, directly elected for a four-year term, is second in authority to the legislature, but he appoints judges and has the power of veto (which can be overturned by a 2/3 vote in parliament).
Chronology:
1911 collapse of Manchu Qing Dynasty; Mongolia declares its independence
1919 China invades Mongolia
1921 with Soviet help, Mongolia gains final independence from China
1924 Mongolian People's Republic declared
1990 pro-democracy protests; Constitution amended; first multiparty elections
1992 second multiparty elections; new Constitution adopted
1996 Democratic Coalition elected as Mongolia's first non-communist government, headed by Prime Minister Enkhsaikhan
1997 N. Bagabandi from the MPRP elected President
Voter turnout:
1996 elections: 92.2 per cent
1996 local Hural: 64.0 per cent
1997 presidential: 85.1 per cent
Mongolia - Society and Culture
Mongolia has a unique and durable traditional culture, centred around the herding lifestyle. Herders remain semi-nomadic, moving their animals with the seasons as they have for centuries
Many urban Mongolians retain strong links to the land, both literal and sentimental, and the country's performing and visual arts often celebrate the landscape and the animals -- especially horses -- that are central to Mongolian life. Mongolia has several distinctive musical instruments and styles, including the morin khuur (horsehead fiddle), the long song (urtyn duu) and the throat-singing style known as khoomi.
After seven decades of communism, Mongolians are once again celebrating their traditional culture, and embracing the image and legacy of the most famous Mongolian of all time - Chinggis Khan, who in the 13th century initiated the Mongol Empire, the greatest land empire the world has ever known. He gives his name to everything from a brand of vodka to a luxury hotel, and centres for academic Chinggis research have been set up.
In sports, Mongolians favour the "three manly sports" -- wrestling, archery and horse racing -- that form the core of the annual festival known as Naadam. Mongolian wrestlers have won a number of medals at international competitions and are even entering the field of Japanese Sumo.
The 1990s have seen a flowering of freedom of expression. Mongolia has an extraordinary 525 newspapers and a wide range of magazines, while the first private radio and television stations have been established.
Religion:
Mongolians have been Buddhists since the 16th century, when the Mongolian king, Altan Khan, was converted by Tibetan lamas. In the pre-revolutionary period, Mongolia was ruled by a series of Living Buddhas, or Jebtzun Damba. The eighth, and last, Jebtzun Damba was removed after the communist takeover.
Traditionally, monasteries were centres both of learning and of power. It's estimated Mongolia had 100,000 monks, or lamas, in 1921 -- one third of the male population. In the 1930s, this power became the focus of a ruthless series of purges that reached a climax in 1937. Most of the country's monasteries were destroyed, and as many as 17,000 monks were killed.
Today, Mongolia is once again embracing its Buddhist heritage. Monasteries are being restored, and are once again crowded with worshippers. The Dalai Lama is an enormously popular figure and has visited the country several times.
For many Mongolians, Buddhism is flavoured with traces of Shamanism, an even more ancient spirituality.
Mongolia also has a significant Muslim community -- about 6 per cent of the population. These are mostly ethnic Kazakhs living in the far west of the country. The opening-up of the country has led to an influx of Christian missionaries, and this remains a source of some tension and debate.
A Young Country:
Mongolia is a remarkably young country -- more than 60 per cent of the population is below the age of 30, and 40 per cent of Mongolians are younger than 16. This young generation, with its embrace of Western styles and ideas, is changing the complexion of the country. Western pop music and North American sports like basketball have a huge following among Mongolia's youth. So, too, do homegrown artists like the pop groups Nikiton and Spike and the singer Saraa.
Social Data:
Television sets: 6.2 per 100 (1995)
Newspapers: 2 per 100 (1995)
Number of telephones: 82,800
Marriage: 10.9 per 1000 over 18
Divorce: 0.7 per 1000 over 18
Number of pensioners: 287,200
Crimes reported: 20,454 (Jan-Oct 97)
As percentage of same period in 1996: 114.4 per cent
Data 1996 unless indicated. Sources: State Statistical Office, Human Development Report Mongolia 1997
Read a story by Jill in The Guardian (9 June 1999): Letter from Mongolia | Herding instinct
Read a World Health Organization (WHO) report on substance abuse and alcohol consumption (WHO Global Status Report on Alcohol 2004) citing Jill here: https://www.who.int/substance_abuse/publications/en/mongolia.pdf?ua=1



© David South Consulting 2018
 Wednesday, February 14, 2018 at 10:44AM
Wednesday, February 14, 2018 at 10:44AM 
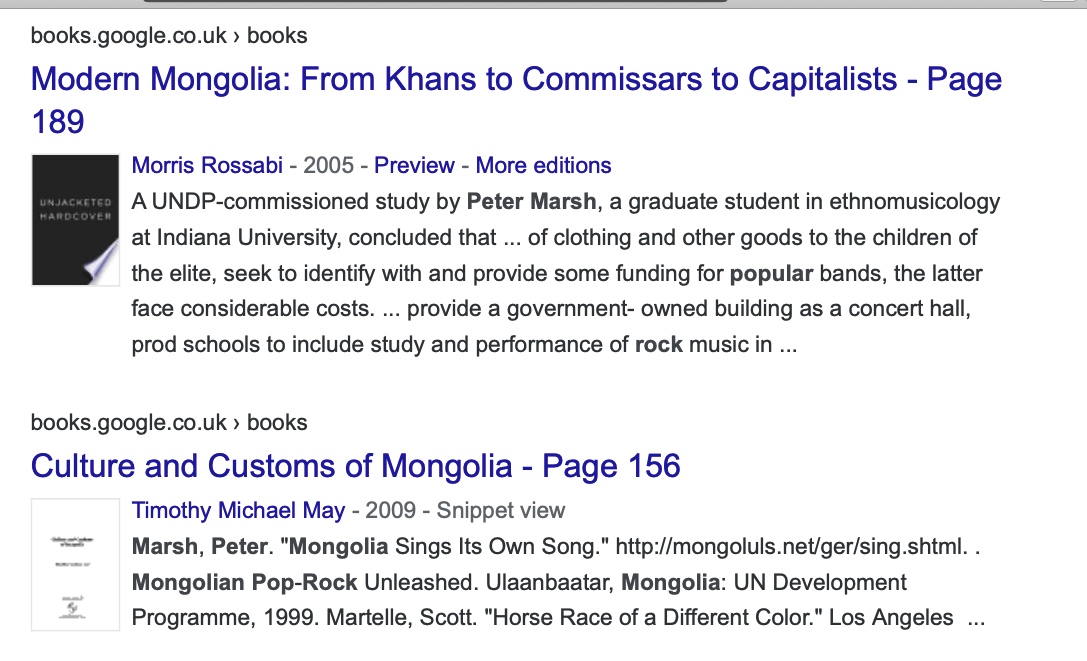 A small sample of books citing the UNDP-funded Mongolian rock and pop book by ethnomusicologist Dr. Peter Marsh.
A small sample of books citing the UNDP-funded Mongolian rock and pop book by ethnomusicologist Dr. Peter Marsh.  Mongoluls.net published an excerpt from the book, "Mongolia Sings its Own Song", from 2002-2007.
Mongoluls.net published an excerpt from the book, "Mongolia Sings its Own Song", from 2002-2007.  Cited in Norovbanzad's Legacy: Contemporary Concert Long Song in Mongolia by Gabrielle Giron (Florida State University Library, 2007).
Cited in Norovbanzad's Legacy: Contemporary Concert Long Song in Mongolia by Gabrielle Giron (Florida State University Library, 2007).  1999,
1999,  B. Bayarma,
B. Bayarma,  Mongolia,
Mongolia,  Mongolian Rock and Pop,
Mongolian Rock and Pop,  N. Oyuntungalag,
N. Oyuntungalag,  Peter Marsh,
Peter Marsh,  UNDP Mongolia Communications Office,
UNDP Mongolia Communications Office,  Youth,
Youth,  book,
book,  business,
business,  entrepreneurship,
entrepreneurship,  free-market economy in
free-market economy in  21st century,
21st century,  Agenda 21,
Agenda 21,  Asian Financial Crisis,
Asian Financial Crisis,  Crisis Response Media,
Crisis Response Media,  David South Consulting,
David South Consulting,  David South International,
David South International,  Digital,
Digital,  Emerging Markets,
Emerging Markets,  Geopolitics,
Geopolitics,  Health and Human Development,
Health and Human Development,  Human Development Innovator,
Human Development Innovator,  ICT4D,
ICT4D,  International Development,
International Development,  Knowledge Sharing,
Knowledge Sharing,  Media,
Media,  Mongolia,
Mongolia,  Mongolian Rock & Pop,
Mongolian Rock & Pop,  Oyuntungalag,
Oyuntungalag,  Shock Therapy,
Shock Therapy,  UNDP Mongolia,
UNDP Mongolia,  United Nations,
United Nations,  Youth
Youth