Sometimes it takes a bold, fresh start to speed up economic and human development goals. Taking a large-scale approach has been used around the world, either establishing new trade zones or even a new city.
Two recent examples in Nigeria and Afghanistan are attempting to speed economic development in their respective countries, with both receiving help from experienced Asian practitioners of rapid economic development.
The role models for this approach are the so-called “Asian Tigers”: they include Taiwan, Hong Kong, Singapore and South Korea. They are admired because each country rose from extreme poverty to become some of the Earth’s richest nations. Importantly, what they did stands as proof that extreme poverty can be escaped from; people can become much wealthier in just a decade or two.
The pioneer of using trade zones to speed development is the Asian city state of Singapore (http://www.gov.sg/government/web/content/govsg/classic/home)..Fifty years ago it was one of Asia’s poorest countries. With its port (http://www.mpa.gov.sg/) it had a way to turn things around but it also realized in the early 1960s it could not just compete by having cheap labour, something that was plentiful across the developing world (http://www.mti.gov.sg/MTIInsights/Pages/Economic-History-and-Milestones.aspx). It needed unique technical skills that could not be found elsewhere.
The country was unable to create products and services that it could export and compete in global markets because of a lack of skills, the Government determined. Authorities employed a mix of measures to make the country attractive to foreign companies to boost skills. These included fair enforcement of local laws, tax incentives and upgraded infrastructure, much of it paid for with an infrastructure tax, rather than borrowing. With the influx of new thinking and high-quality skills, new technologies and new ways of doing things, in time, a culture of innovation became hardwired into the way things were done in Singapore.
Beginning in 1961 with the Jurong Industrial Estate (http://infopedia.nl.sg/articles/SIP_246_2004-12-16.html), the Singapore government set aside land to develop the economy by attracting international businesses and boosting its existing port facilities. It also established the Economic Development Board (EDB) in 1961 and the Singapore Tourism Promotion Board (STPB) in 1964.
By creating favorable conditions for international businesses to come in and operate, Singapore quickly developed to become one of Asia’s wealthiest trading and manufacturing centres.
This is a strategy China successfully implemented in the 1980s and 1990s and in turn generated the largest and quickest population shift out of poverty in human history, turning the country into an economic powerhouse.
The secrets to making this strategy work include understanding what modern infrastructure requirements are necessary for international businesses. These days, this means speedy and generous bandwidth for the Internet, modern airports, roads, security, and quality housing and food.
One of the biggest contemporary challenges is competition. Whereas Singapore was a pioneer in its day, now, many countries across the global South are pursuing this strategy to spur growth. An international company has many options to consider, and will more than likely gravitate towards the country that makes the best offer with the least risk.
Trade zones are places ripe with opportunity for innovators. New places tend to be seeking the latest in information and communication technologies, the latest in transportation options, modern housing and office facilities. All of these changes require innovators with fresh thinking to make them work. It is also often easier to introduce new ways of doing things to places that are not coping with legacy infrastructure and old habits and ways.
Billing itself as a “new model city,” the Lekki Free Zone Lagos, Nigeria (lekkizone.com) in West Africa is trying to bring a fresh start to the city and the region. It is a joint partnership between investors from China and Nigeria.
Its goal is to better connect regional markets to the global economy. The free trade zone hopes to remove barriers to growth and to attract international investment, becoming the top destination for inward investment in Africa. The project is being run by the Lagos State Government but funded with private capital investment.
Nigeria has been looking into Free Zones since 1982, as it sought additional ways to earn income apart from oil exports. The Export Processing Zone Act 63 was passed in 1992 and the Calabar Export Processing Zone was eventually set up in 1999 (http://www.nepza.gov.ng/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=18&Itemid=34). Since then, a slew of Free Zones have been set up, or are in the works.
The Lekki Free Zone is envisioned as a high-tech zone that will eventually lead to the creation of 2 million jobs. The Zone’s investors are targeting businesses working in oil and gas, petrochemicals, electronics, light and heavy equipment, machinery and automobiles, pharmaceuticals, textiles, shopping and banking and financial services.
Lagos State is home to 21 million people, and the current city of Lagos is on course to become the third-largest megacity in the world. Officials claim the area has an economic growth rate of 16.8 per cent per year.
The 16,500 hectare Lekki Free Zone, to the southeast of the city, is divided into two parts: an industrial zone and a residential zone. The residential zone will include apartments and villas, shopping malls and plazas, hospitals and clinics, schools and research and development centres and a hotel, tour and recreational centres, golf courses, gyms and water sports facilities.
Located on the southern coast of Nigeria with connections to the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Guinea, the Lekki Free Zone says it will give companies access to the largest consumer market in Africa, with a potential reach of 500 million people.
The companies will also be able to draw on Nigeria’s natural resources, including oil, natural gas, timber, rubber, cocoa, Arabic gum and sesame seeds as examples.
Another new beginning is being sought in war-torn Afghanistan, which is working on building a new city close to the capital, Kabul.
Kabul New City started construction in 2013 and is planned to be a city of canals, parks and villas. It will be home to 1.5 million people, cost US $33 billion and take 15 years to complete. It is being partly funded by Japan.
It is a very ambitious scheme for a country that has been mired in conflict for decades. It is hoped the initial seed capital invested by Japan will attract other investors to fully fund the project. Japan got the project going with a commitment to contribute US $106 million between 2009 and 2015.
The site of Kabul New City is 19 kilometres from the existing Kabul, near the Bagram airbase used by NATO forces in the country.
Foreign military forces are looking to leave Afghanistan in 2014 and the new city offers a fresh start for the country after years of conflict.
Located in an area surrounded by the Marko mountains, it is in “one of the safest areas of Afghanistan,” Abdul Habib Zadran, Chief Financial Officer of the Dehsabz-Barikab City Development Authority (http://www.dcda.gov.af/), the agency in charge of the project, told The Sunday Times.
The project could be a significant leap ahead in modernization from the current conditions in Kabul, where the streets are in poor condition and buildings in disrepair. Kabul was originally built for 800,000 people, according to The Sunday Times, but now has over 4 million residents. Projections forecast the city growing to 6.5 million people by 2025. Kabul will experience extreme pressure to handle this growing population and find the resources to serve it.
The homes would receive electricity from solar panels and renewable energy sources. Kabul New City will need to tackle the problem of access to enough water to service the growing new city’s population. Plans are afoot to provide water from rivers north of the city.
The master plan for the new city has been designed by Zahra Breshna (breshna-consulting.com), an Afghan-German company which has also built the new Kabul Bank headquarters. The company calls the project “a new beginning for Kabul.”
By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions
Published: May 2013
Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP's South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South's innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.
Follow @SouthSouth1
Google Books: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=RfdcAwAAQBAJ&dq=development+challenges+may+2013&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Slideshare: http://www.slideshare.net/DavidSouth1/development-challenges-may-2013-issue
Southern Innovator Issue 1: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Q1O54YSE2BgC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 2: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Ty0N969dcssC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 3: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=AQNt4YmhZagC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 4: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=9T_n2tA7l4EC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 5: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=6ILdAgAAQBAJ&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s

This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
 Monday, November 6, 2017 at 11:05AM
Monday, November 6, 2017 at 11:05AM 
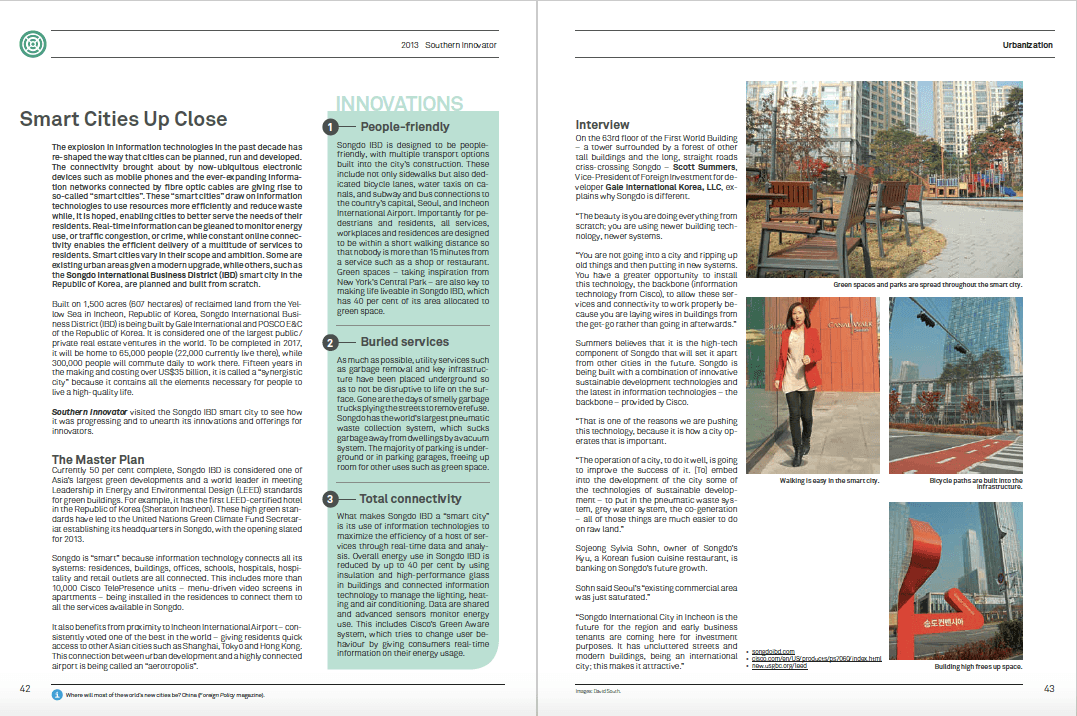 Smart Cities Up Close in Southern Innovator Issue 4.
Smart Cities Up Close in Southern Innovator Issue 4. 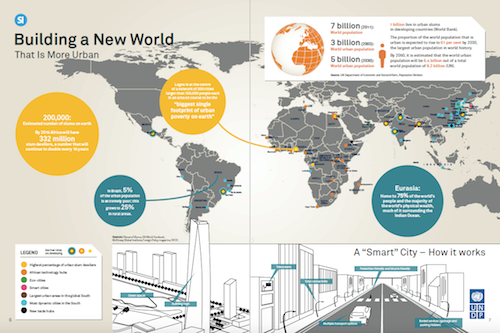
 Southern Innovator Issue 4 contents.
Southern Innovator Issue 4 contents. Southern Innovator Issue 4: Cities and Urbanization is published by the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC).
Southern Innovator Issue 4: Cities and Urbanization is published by the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC).  The first five issues of Southern Innovator. The highly influential magazine was distributed around the world and each issue was launched at the annual Global South-South Development (GSSD) Expo hosted by the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC).
The first five issues of Southern Innovator. The highly influential magazine was distributed around the world and each issue was launched at the annual Global South-South Development (GSSD) Expo hosted by the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC). David South,
David South,  Smart cities,
Smart cities,  Songdo,
Songdo,  South Korea,
South Korea,  Southern Innovator,
Southern Innovator,  UNDP,
UNDP,  digital,
digital,  global South,
global South,  information technology,
information technology,  infrastructure,
infrastructure,  smart,
smart,  urban in
urban in  David South Consulting,
David South Consulting,  Development Challenges, South-South Solutions,
Development Challenges, South-South Solutions,  GSSD Expo,
GSSD Expo,  Global South-South Development Expo,
Global South-South Development Expo,  Southern Innovator Magazine,
Southern Innovator Magazine,  UN Innovator Stories,
UN Innovator Stories,  UNDP Innovator Stories,
UNDP Innovator Stories,  UNOSSC
UNOSSC 
