Mongolia Prepares for a Magazine Explosion | 1998
 Tuesday, June 5, 2018 at 2:18PM
Tuesday, June 5, 2018 at 2:18PM 
Ulaanbaatar (Mongolia) - Mongolian newsstands are bursting at the seams. But while the content of the country's publications is varied, their form is not. Newsprint rules this country's publishing industry. The few glossy magazines for sale are imports from Russia.
When the democratic revolution unleashed the tide of free expression in the early 1990s, a flood of newspapers poured forth. It made sense. The cheap-and-cheerful technology of newsprint is low-tech, accessible and inexpensive. Suddenly everyone could be a publisher.
But Mongolia's increasingly sophisticated media landscape is about to go "glossy". Tomorrow (September 9) sees the launch of Ger (Home), Mongolia's first on-line magazine. A bilingual quarterly funded by the United Nations, it combines entertainment - articles on the changing sexual attitudes of young Mongolians and the country's vibrant pop scene - with information on the work of the UN and other NGOs in Mongolia.
"We want something that will tell the stories of Mongolians and their experiences over the last eight years - both to Mongolians and to the rest of the world," says David South, communications coordinator at the United Nations Development Programme.
This month also brings the premiere issue of Tusgal (Strike), billed as the first full-colour, general-interest magazine in the new Mongolia. Published by Mongol News Company - the privately owned media group whose stable of publications includes the daily newspaper Onoodor and The UB Post - it offers a lively mix of sport, culture and celebrity articles, also aimed primarily at the young.
These two publications are just the top of the stack. Mongolia's two best-known printing houses, Admon and Interpress, are said to be working on titles of their own.
Mongolia's quick-to-learn capitalists see a gap - and they want to fill it.
"In Mongolia there are many newspapers, but no world-class magazines," says Tusgal's editor-in-chief, Do. Tsendjav. "On the streets you can see a lot of publications that aren't exactly magazines but you can't call newspapers, either - newspapers that appear every 10 days or two weeks.
"We want to fill this space. We want to produce the first colour magazine that will reach world standards, something close to Time or Newsweek."
"There's an enormous thirst for quality journalism, quality publications that are interesting to look at, top photojournalism - all the things newspapers don't cover," adds South.
"We've seen newspapers moving to more colour, more photographs, and that shows a desire for quality."
That quality comes at a price. Tusgal, with 70 colour pages, will sell for between Tg 1500 and Tg 2000 - not much cheaper than an American publication like Time, and too expensive for many Mongolians.
With only 1000 Internet subscribers in Mongolia, Ger has an even smaller market within the country - though South is quick to point out, the UN has established public-access Internet centres in Ulaanbaatar and several aimags.
And he says a print version is planned to follow.
"Distribution is the big problem right now," he says.
"We have to see how we can organize distribution to reach the whole country. I know more magazines will be launched soon in Mongolia, and hope a distribution network may grow out of that."
The editors know Mongolia's magazine market and magazine technology are in their infancy. Although companies like Admon and Interpress get more sophisticated equipment by the month, the capacity to produce quality publications is still limited - the first issue of Tusgal has been printed outside Mongolia.
Human resources need to develop as well, Tsendjav admits.
"To produce a monthly magazine you need highly qualified journalists. We don't have that right now. We're still seeking them out."
But he is confident this will change - and quickly, too, if the pace of development in the past eight years is anything to go by.
"During socialism, Mongolia had many magazines, but it all stopped after 1990," notes Tsendjav. "It was a question of economics.
"At first we don't think we can earn money from this. If you want to make money you have to wait two or three years. So what we are aiming for at first is to build a readership.
"I think in two or three years, living standards will improve. People will have more money to spend on things like magazines. But we don't want to wait for people to get enough money. We want to be the first, so people will develop an interest.
"There will be competition. Nowadays a lot of business-people understand the importance of the media. I welcome competition. It'll make us work harder. It's good for everybody."
From In Their Own Words: Selected Writings by Journalists on Mongolia, 1997-1999
Read a story by Jill in The Guardian (9 June 1999): Letter from Mongolia | Herding instinct
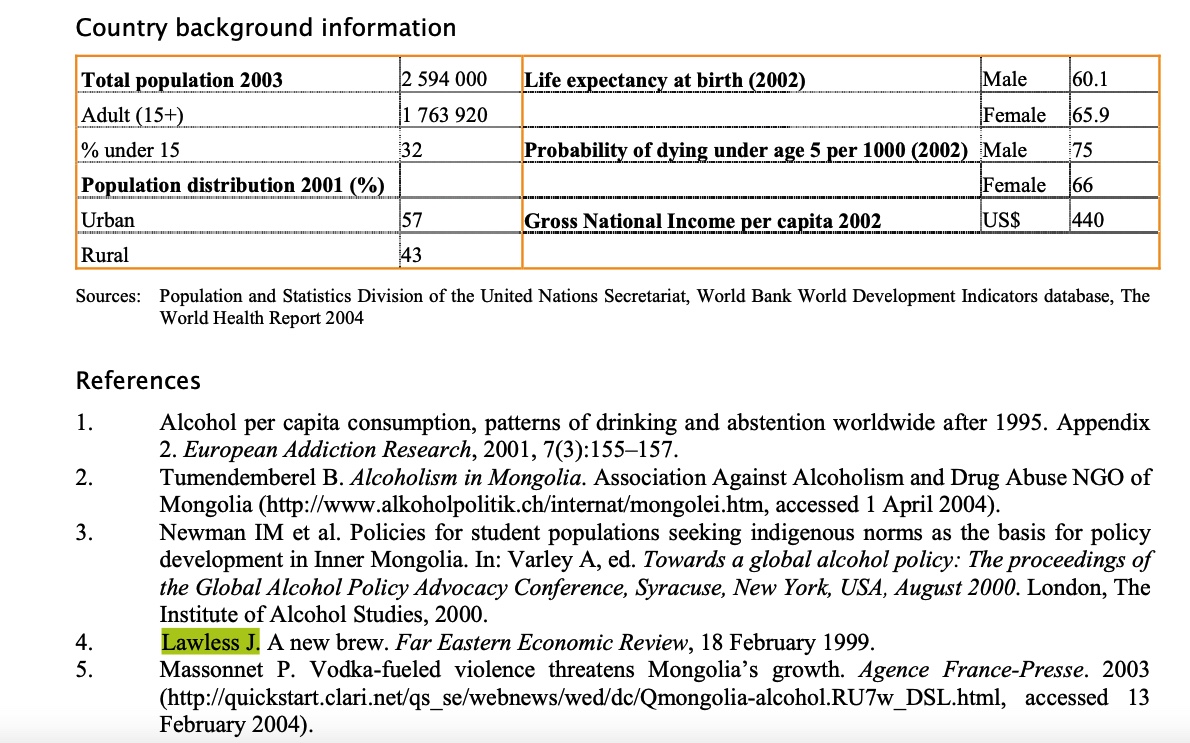 Jill's story for the Far Eastern Economic Review is cited in the WHO Global Status Report on Alcohol 2004.
Jill's story for the Far Eastern Economic Review is cited in the WHO Global Status Report on Alcohol 2004.
 Wild East: Travels in the New Mongolia by Jill Lawless offers a vibrant account of what it was like to be a journalist in Mongolia in the late 1990s.
Wild East: Travels in the New Mongolia by Jill Lawless offers a vibrant account of what it was like to be a journalist in Mongolia in the late 1990s.
ORCID iD: https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5311-1052
© David South Consulting 2018
 David South,
David South,  David South Consulting,
David South Consulting,  Ger,
Ger,  Jill Lawless,
Jill Lawless,  UN,
UN,  colour,
colour,  digital,
digital,  internet,
internet,  magazine,
magazine,  media,
media,  newspapers,
newspapers,  online in
online in  Austerity,
Austerity,  Cities,
Cities,  David South Consulting,
David South Consulting,  Digital,
Digital,  Media,
Media,  Shock Therapy,
Shock Therapy,  UB Post,
UB Post,  UNDP,
UNDP,  UNDP Mongolia,
UNDP Mongolia,  Youth
Youth 


