By David South
Today’s Seniors (Canada), April 1993
Check your prejudices at the door, look beyond your self-interest, and open your mind, because the Grey Panthers are here in Canada.
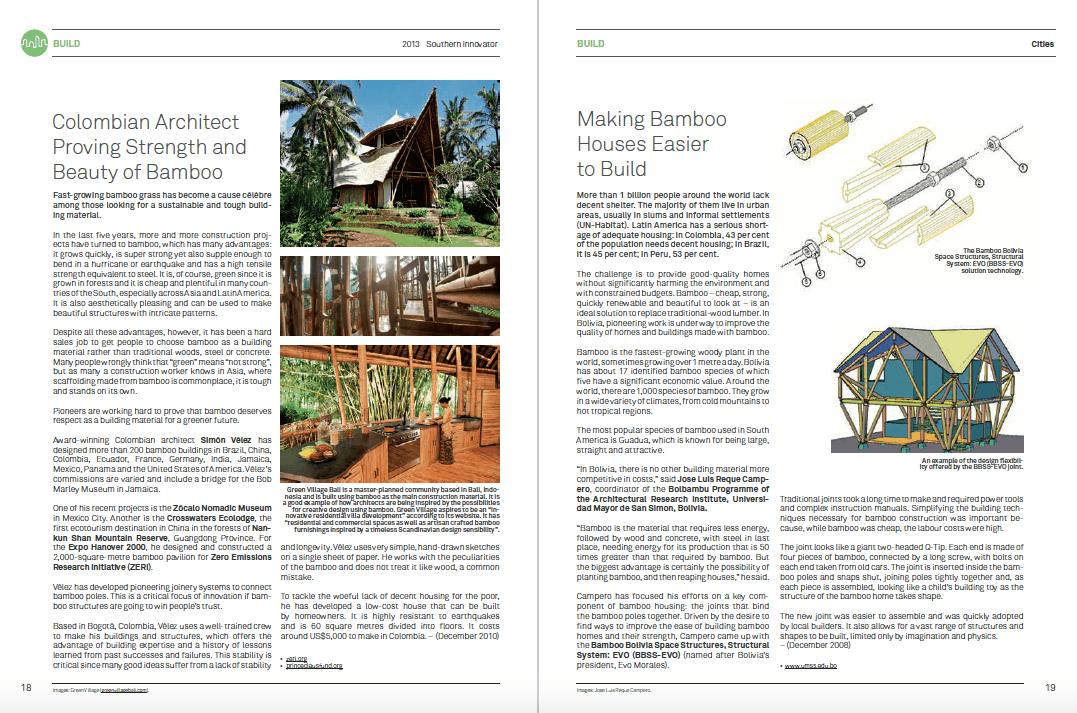
Joe Moniz, the 26-year-old founder of the Canadian Grey Panthers, is confident that his ambitious plans for a new national seniors’ organization are just what Canadian seniors need.
That’s right: 26-years-old. Modelled on the U.S. Gray Panthers, the Canadian Grey Panthers believe in harnessing the power of all age groups, making the connection that everybody will eventually be a senior and that seniors benefit from a better society for everyone.
“The major difference between us and any other organization is our slogan, “Age and Youth Working Together,” he says. “Look at our pension fund. It’s depleting. I’m concerned about my future as a senior citizen - will there be a pension fund? We want to act now, to bring youth and age together to improve the situation of seniors today and improve our situation in the future.
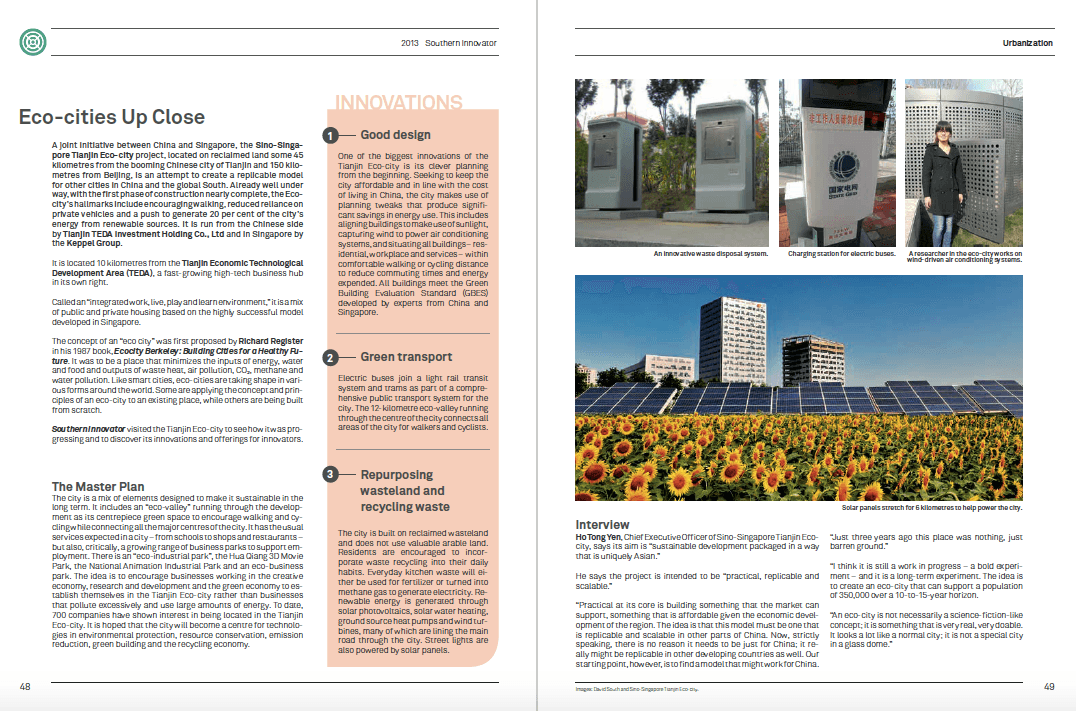
“Membership is open to all age groups. We want to bring seniors into day care to interact with children. We want to deal with the universities, give people the opportunity to discuss and unite. It’s a different approach, but it can make a huge difference.”
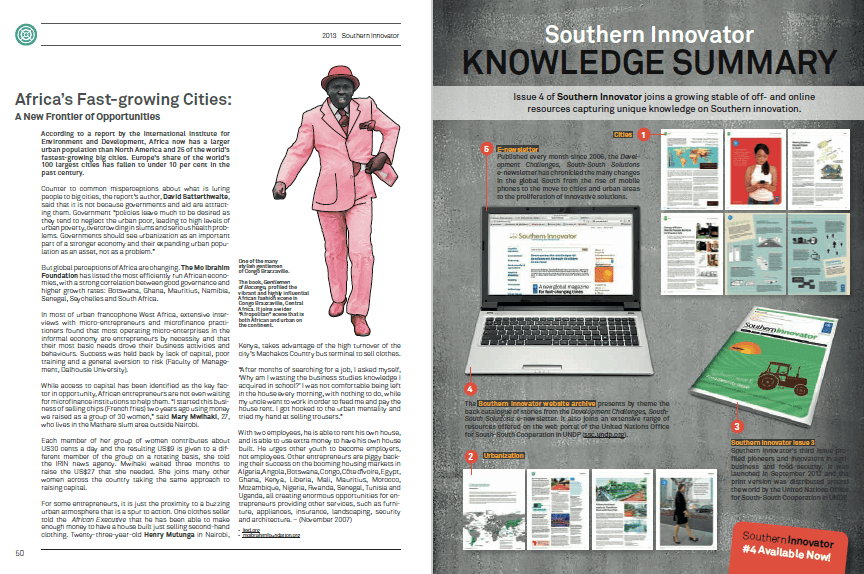
Moniz has already organized the group’s first chapter, in Hamilton, complete with a board of retired university professors and doctors. The group has put together insurance packages that will “blow the others out of the water.”
“All seniors’ attempts at lobbying in the past have been short term,” says a blunt Moniz. “We are the organization that will make the difference. We will lobby provincially, federally, and municipally, and we are non-partisan.
“The reason I’m introducing the Grey Panthers is to keep grey power alive in Canada, and to provide the necessary channels to do so through lobbying efforts. If anyone has problems with local politicians, they can call us, and we in turn let them know the channels they should use. There are a lot of seniors out there being cheated, and it is up to us to help them.”
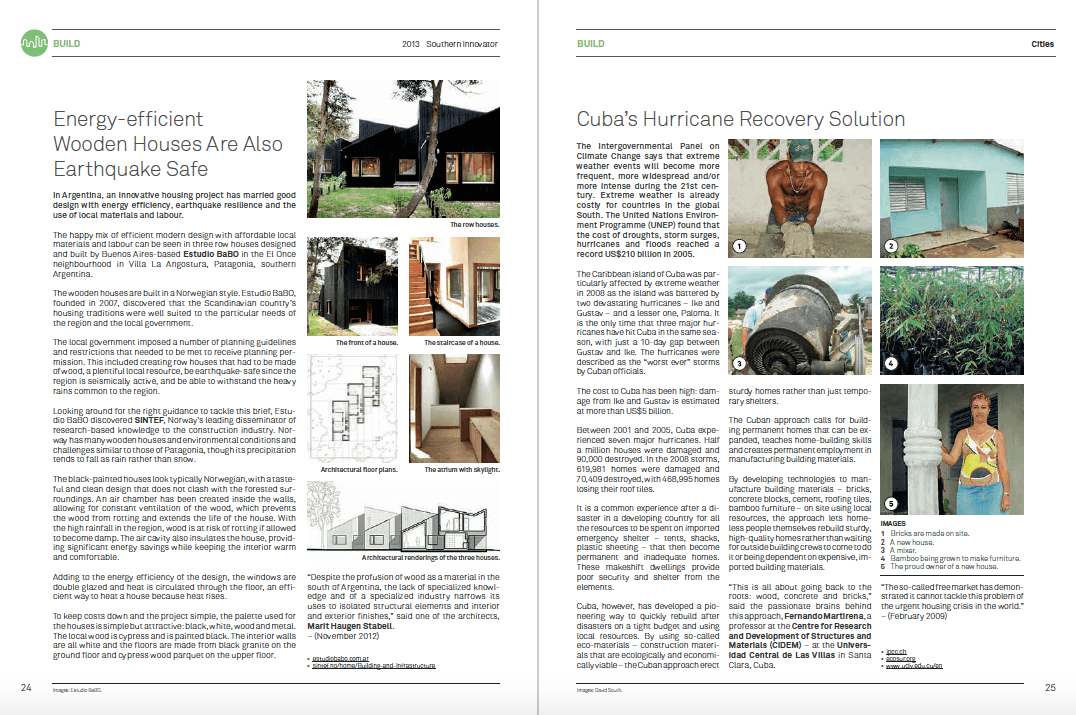
The Canadian Grey Panthers (which uses the British spelling, as opposed to its American counterpart) will initially concentrate on four issues: pensions, drug plans, affordable housing and long-term care, and will communicate information through newsletters, surveys and meetings.
Moniz promises to make the Panthers accessible to all, no matter what their income. He plans to hit the streets and visit institutions to inform seniors of the group’s presence. As if to prove the group’s potential for excitement, an enthusiastic gentleman from a local retirement home interrupts Moniz during a coffee shop interview. “That’s the best thing I’ve heard from a young person in Toronto,” he says.
The U.S. Panthers were formed by political activist Maggie Kuhn and five friends in 1970. Back then, their name wasn’t as exciting. It was the convoluted and unsexy “Consultation of Older and Younger Adults for Social Change.” In 1972, they adopted the media’s pet name - a grey twist on radical African-American rights organization the Black Panthers.
The radical milieu of political activism was contagious - and the Panthers symbolized its jump from the youth of America to other generations.
“When we formed, we were an intergenerational group,” says Panthers’ U.S. national chair, Charlotte Flynn. “The first issue the group addressed was mandatory retirement. We combat the stigma of ageism, which is making decisions about people based on chronological age. Ageism isn’t just confined to the elderly - ageism exists for young people as well.”
The agenda of the Panthers is just as radical today. Flynn, who is candid about the group’s failures as well as its successes, admits that it isn’t the easiest route to popularity. With membership at about 45,000, the U.S. Panthers have spoken out on now-popular issues like health care, the environment, affordable housing - and taken brave stands against mainstream opinion when it came to the Gulf War and the invasion of Panama.
And they think big. Not content with just influencing the American political scene, the Panthers have taken on the world, gaining official advisor status at the United Nations.
Although involved in a broad range of issues, Flynn says the Panthers are primarily seen as a strong voice for the rights of American seniors.
“We have tried very hard to let people know we are not a special interest group for the elderly,” says Flynn. “But we are always getting called upon to highlight what any legislation is doing to older people.”
With Panther groups sprouting in Europe and now in Canada, the important issue of maintaining the integrity of the Panther name has arisen, says Flynn. She points to the flip side of having a reputation for action: people want to start branches without being interested in the full agenda of the Panthers, using the name for shock value. At the last convention in November 1992, the Panthers formed a committee to act as quality control monitors for the name.
One thing is clear from the ambitious agenda of the Grey Panthers - they aren’t for everyone.
But Moniz’s pragmatic approach seems distinct from the American Panthers. He shies away from some of the American group’s positions, emphasizing a balance between insurance policies and political policies.
“If you read the American Panthers’ position sheet, it’s anti-this and anti-that,” he says. “We aren’t going to take that approach. It would be suicide.”
But he is quick in his praise of the group and its founder Maggie Kuhn. “People may consider her actions to be radical, but they’re not. Look at the achievements. She is one of the top 25 active women in the U.S.
“The Gray Panthers are achievers. They have proven the effectiveness of intergenerational attempts at social justice.”
A quick call to seniors’ groups drew many surpised faces.
“I can’t say anything about them - I don’t know who they are,” responded Murray Morgenthau, executive director of the Canadian Association of Retired Persons (CARP).
Jane Leitch at the United Senior Citizens of Ontario had heard something was happening but wonders why a new group is forming “with so many groups out there.”
One Voice spokesperson Andrew Aitkens says his group is closer to the American Association of Retired Persons than the Panthers in their approach, and that they “have found that there are much more effective ways for advocacy. We don’t march on the Hill at the drop of the hat.”
But Flynn says the Panthers embody a philosophy distinct from all other seniors’ groups. “As Maggie Kuhn said, ‘those of us who are older are the elders of the tribe and should be concerned about survival.’ We look at all issues that deny people the ability to realize their full potential, whether young or old. We are really interested in empowering people rather than being a special interest for the elderly.”
Note: In the early 1990s, I was an Investigative Medical and Health Correspondent for Today's Seniors. This involved contributing the lead story for each issue of the paper. Concerns around the state of the health system during a time of austerity and government cuts (Ontario was experiencing what has been later called an economic crisis akin to a depresssion) and re-organizations, meant the stories always had a high profile with readers. I regularly covered Health Ministry announcements from the Ontario Legislature, interviewed ministers, and travelled to the US to cover developments down there. I drew on my experience working in the health system, my knowledge of medical history from my degree studies at the University of Toronto, my communications work at the Hannah Institute for the History of Medicine, and my routine trawling through journals at the University of Toronto (this was before easy access to the Internet!) to break news stories on medical and scientific developments. This experience proved extremely useful when I later had to respond to the unfolding crises (austerity, economic crash, Asian Financial Crisis, HIV/AIDS/STDs etc.) in Mongolia while working for the United Nations (1997-1999). I also learned about many innovations that were being deployed in Ontario to respond to the crisis in the health system, something I also found very useful for my work with the UK's NHS in the early 2000s.
Read more stories from Today's Seniors here:
Critics Blast Government Long-Term Care Reforms
Cut Services to Elderly, Says Doctors' Survey ... But Leave Our Salaries Alone!
Feds Call for AIDS, Blood System Inquiry: Some Seniors Infected
Government Urged to Limit Free Drugs for Seniors
Health Care on the Cutting Block: Ministry Hopes for Efficiency with Search and Destroy Tactics
Private Firms Thrive as NDP 'Reinvents' Medicare
Psychiatric Care Lacking for Institutionalized Seniors
Seniors Falling Though the Health Care Cost Cracks
Specialists Want Cancer Treatments Universally Available
 Wednesday, December 30, 2020 at 3:02AM
Wednesday, December 30, 2020 at 3:02AM 

 In 1998 Der Spiegel's "Kommunikation total" issue profiled the global connectivity revolution underway and being accelerated by the Internet boom of the late 1990s. It chose my picture of a satellite dish and a ger in the Gobi Desert to symbolise this historic event.
In 1998 Der Spiegel's "Kommunikation total" issue profiled the global connectivity revolution underway and being accelerated by the Internet boom of the late 1990s. It chose my picture of a satellite dish and a ger in the Gobi Desert to symbolise this historic event. 1998,
1998,  David South,
David South,  Douglas Gardner,
Douglas Gardner,  Gobi desert,
Gobi desert,  UNDP,
UNDP,  UNDP Mongolia Communications Office,
UNDP Mongolia Communications Office,  austerity,
austerity,  crisis,
crisis,  poverty,
poverty,  shock therapy,
shock therapy,  transition,
transition,  women in
women in  Agenda 21,
Agenda 21,  Austerity,
Austerity,  Blue Sky Bulletin,
Blue Sky Bulletin,  Data,
Data,  David South Consulting,
David South Consulting,  Environment,
Environment,  Magazine Stories 1990s,
Magazine Stories 1990s,  Northeast Asia,
Northeast Asia,  Poor,
Poor,  Shock Therapy,
Shock Therapy,  Solutions,
Solutions,  Sustainable Development,
Sustainable Development,  Trade,
Trade,  UN Innovator Stories,
UN Innovator Stories,  UNDP,
UNDP,  UNDP Innovator Stories,
UNDP Innovator Stories,  UNDP Mongolia,
UNDP Mongolia,  United Nations,
United Nations,  United Nations Mission,
United Nations Mission,  Women
Women