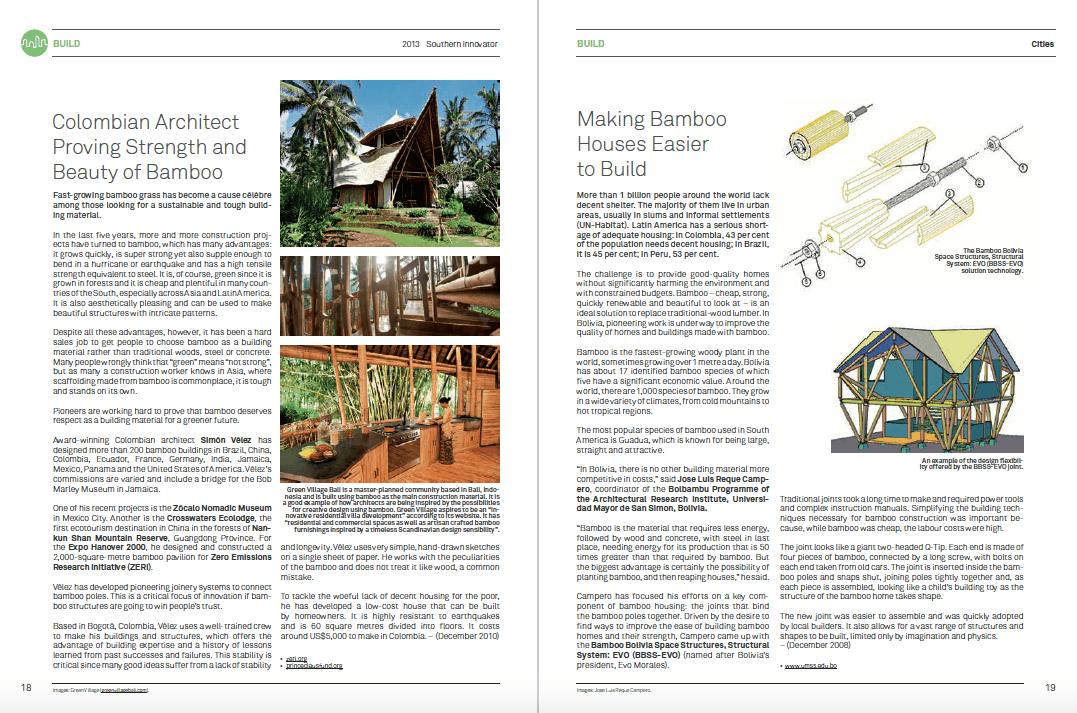
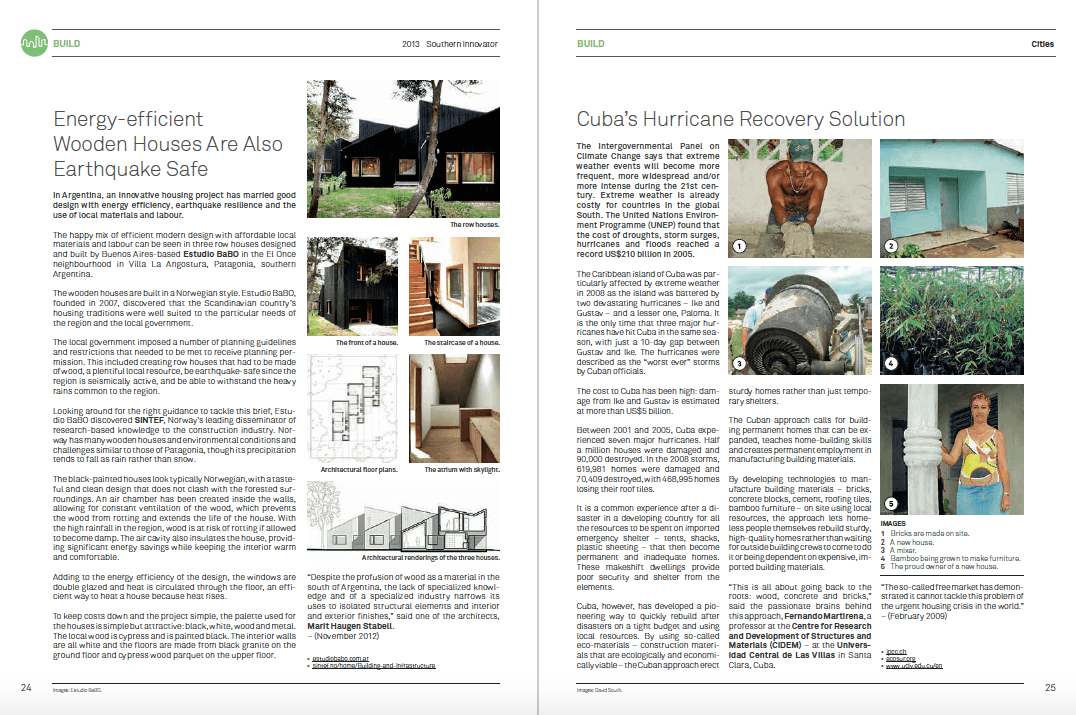
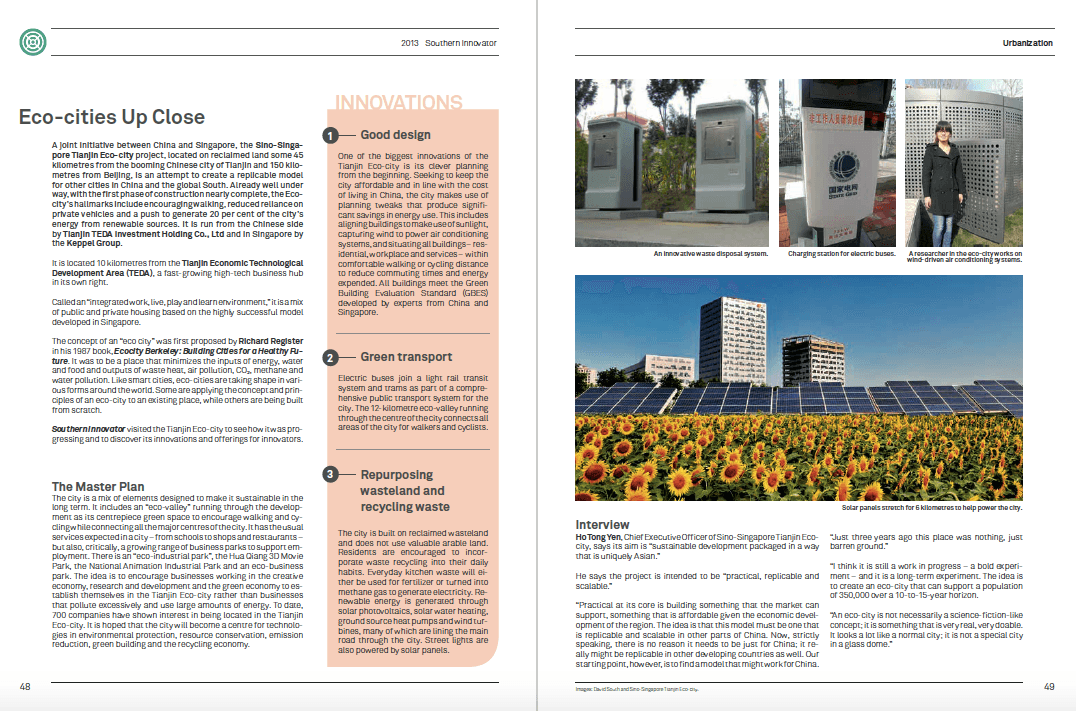
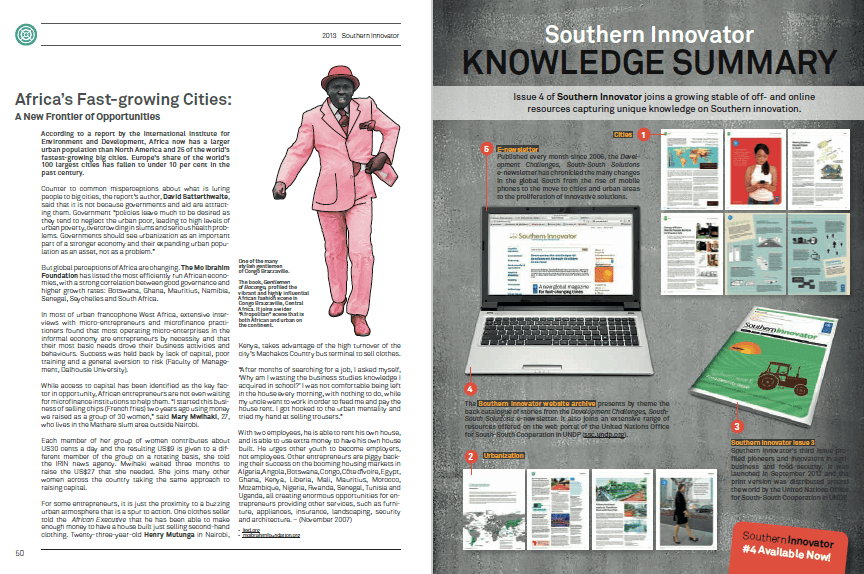
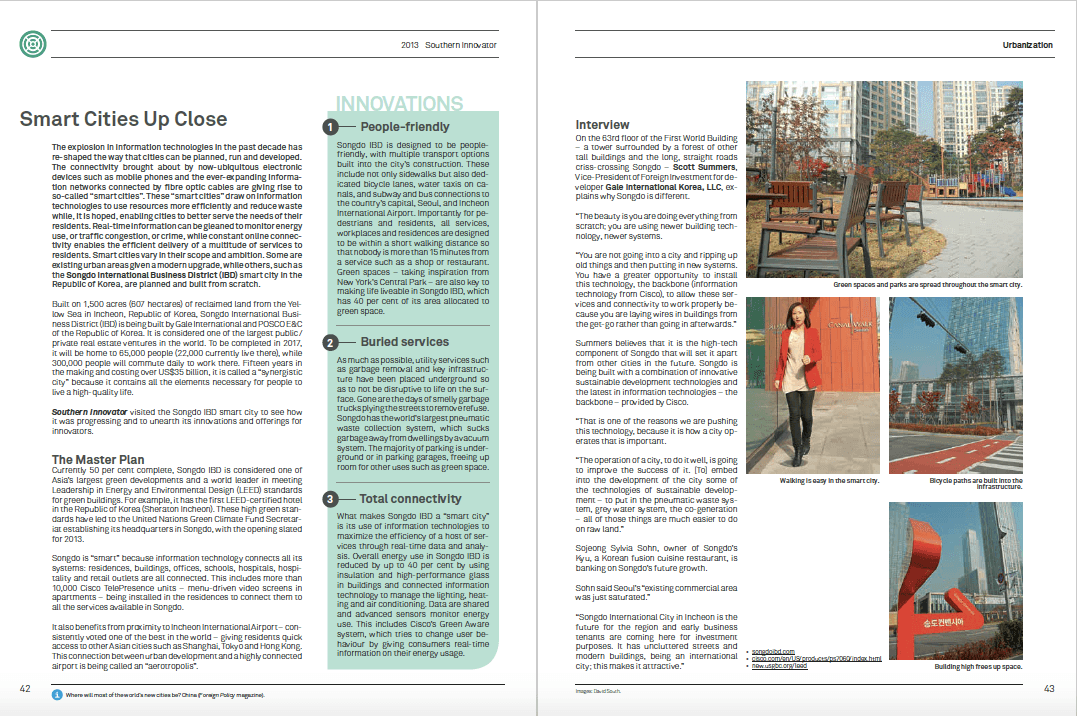
The world’s population is heading towards 9.6 billion by 2050 (UN). Combined with a growing middle class and rising living standards across the global South, that means ever-greater demand on the world’s finite resources. This raises a crucial question: Where will the energy to power rising living standards come from, and how much damage will be done to the planet’s environment by pollution created generating it (https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/news/population/un-report-world-population-projected-to-reach-9-6-billion-by-2050.html)?
The solution advocated by the world’s scientists is to move to sustainable energy creation, which does not rob from the future to create energy for today.
Such an approach requires fresh thinking and engagement from those who are actually involved in the struggle to raise living standards and improve human development.
One way to do this is to use high-profile awards and prizes to lure out fresh thinking and innovators and help them get the funding they need to realize their plans.
The International Ashden Awards (ashden.org) – considered the “leading green energy awards” – is about championing and promoting “practical, local energy solutions that cut carbon, protect the environment, reduce poverty and improve people’s lives”. It recently announced the finalists and winners for 2014.
The international finalists are 10 sustainable energy enterprises drawn from Africa (Burkina Faso, Tanzania), India and Southeast Asia (Cambodia, Myanmar). A handy, clickable and searchable online map (http://www.ashden.org/winners) further explains the winners and finalists for 2014 and previous years.
“With the stark warnings from the IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) of the impacts of climate change, especially for the most vulnerable, we need to find solutions before it is too late,” said Ashden founder-director Sarah Butler-Sloss.
“Our role at Ashden is to shine a light on those organizations around the world that are helping reduce carbon emissions and finding ways of adapting to the effects of climate change.”
The mix of non-profit organizations and businesses among 2014’s winners and finalists shows there is no shortage of enthusiasm and fresh thinking out there. Proof the global South is alive with innovators with solutions.
Among the five international winners – who will receive between US $8,566 and US $68,531 each – is India’s Greenway Grameen (greenwaygrameen.com). It is tackling the problem of harmful pollution caused by cooking. Despite rapid economic growth and the spread of consumer goods such as televisions and mobile phones, most Indian women still cook with wood or dung. This is not only time-consuming, it also produces health-damaging smoke. Greenway Grameen was founded by two young MBA graduates in 2010 to make and sell affordable, desirable cookstoves that reduce smoke, cook food more quickly and stay cleaner for longer, dramatically improving the quality of life for many women and girls. As of March 2014 more than 120,000 of Greenway’s made-in-India smart stoves had been sold, benefitting around 610,000 people.
Another Indian winner is Infosys (infosys.com). India’s fast-growing economy is making ever-greater demands on its electrical grid. Global IT giant Infosys is leading the way to more sustainable growth by embracing green building measures, decreasing electricity consumption per staff member across its Indian business campuses. Success lies in seizing every opportunity to cut energy consumption in its existing buildings – from reducing the size of chiller plants for air conditioning to painting roofs white to reflect the heat. Cutting-edge design of new buildings also helps keep offices cooler and maximizes natural light. Taking US $80 million off its electricity bills, Infosys has proven the business case for large companies to invest in energy efficiency – not just in India but around the globe.
Among the other winners:
– Tanzania’s Off Grid Electric (offgrid-electric.com) is a leader in solar energy in East Africa, using mobile money to sell solar power as a daily service at an affordable price. Mobile money – where customers pay with their mobile phones – is increasingly used as a method of payment. Off Grid stands out because it understands the importance of customer service, offering an all-day customer care telephone line and ongoing support from a local agent. More than 10,000 households have taken up the service since April 2012. As fast as systems are manufactured they are off to customers – thanks to a sophisticated mobile phone app-based customer registration and product-tracking system.
– Myanmar’s Proximity Designs (proximitydesigns.org) is introducing treadle pumps (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Treadle_pump) and other sustainable agriculture technologies to the country for the first time. Lifting water from wells and carrying it across fields is back-breaking, time-consuming work for rural farmers. Combined with water-saving drip irrigation technology, foot-operated treadle pumps that draw up water from wells can dramatically increase yields and incomes. Farmers are now seeing their lives transformed with some harvests and incomes more than doubling – and the pumps are helping ease the daily drudgery of farming. With over 90,000 households benefiting so far, Proximity Designs continues to adapt and introduce new products like solar pumps, to meet the needs of this rapidly changing country.
– Cambodia’s Sustainable Green Fuel Enterprise (http://www.sgfe-cambodia.com/environment) is turning leftover coconut shells and other waste into clean-burning briquettes for use as cooking fuel in the capital Phnom Penh’s homes and restaurants. While most Cambodians cook on wood charcoal, contributing to the country’s rampant deforestation and air pollution, this pioneering Cambodian business – led by Carlo Figà Talamanca – can scarcely keep up with demand.
The finalists are also an innovative lot too. Kéré Architecture (kerearchitecture.com) in Burkina Faso, Africa, has set a new standard for green school buildings. The school it built has a ventilated roof and other clever design features, providing a much cooler environment for children to study in. Not only that, the school was built by local people, and largely with local materials. Germany-based Francis Kéré, originally from Burkina Faso, designed and built the school in his home village. Kéré Architecture has since designed and built more than 20 innovative, naturally cooled public buildings in Africa.
India’s Sakhi Unique Rural Enterprise (sureindia.co.in), or SURE, is a not-for-profit social enterprise in central Maharashtra that has selected, trained and supported more than 600 female micro-entrepreneurs to sell clean energy products such as solar lanterns and cleaner cookstoves to other women. For the women entrepreneurs, selling energy products boosts income and carries a social cachet, while customers also see their lives improved with time-saving products.
Another Indian innovator, Mera Gao Power (http://meragaopower.com/), is demonstrating the business case for meeting the needs of some of the poorest people in India with unsubsidized commercial micro-electric grids, connecting more than 20,000 Uttar Pradesh families to clean, affordable power. Each system is easy to install and provides seven hours of light and mobile phone-charging for up to 32 houses. And with weekly payments of just US $0.42 cents, the electricity is even cheaper than kerosene.
The Rajasthan Horticulture Development Society (http://horticulture.rajasthan.gov.in/) in India has come up with a novel way to boost green agriculture and boost farming incomes. Farmers in the desert state of Rajasthan are seeing their sons return from cities to work on their farms thanks to a new solar-powered agricultural boom. The Rajasthan Horticulture Development Society (RHDS) has provided more than 10,000 farmers with new solar-powered water pumps, enabling year-round cultivation of high-value crops and the kind of high-tech horticulture that’s never been seen in the region before. With farmers’ incomes more than doubling, the programme has given them the “gift of life”.
And finally, Tanzania’s SimGas (simgas.com) is selling biogas plants that help people turn manure into clean gas for cooking instead of using charcoal, helping reduce deforestation. The plants are factory-produced and made of plastic, so they can be installed much more quickly than conventional plants and reach many more thousands of people. SimGas has just installed the largest plastic injection-moulding machine in East Africa, creating the potential to roll out biogas plants across East Africa.
The Ashden Awards were set up in 2001 to champion trailblazing sustainable energy enterprises and programmes that improve people’s lives and tackle climate change. Ashden says its 150 award winners have improved the lives of 37 million people worldwide, and are now saving over 5 million tonnes of carbon emissions every year.
By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions
Published: July 2014
Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP's South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South's innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.
Follow @SouthSouth1
Google Books: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=qBU9BQAAQBAJ&dq=development+challenges+july+2014&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Slideshare: http://www.slideshare.net/DavidSouth1/development-challenges-july-2014-published
Southern Innovator Issue 1: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Q1O54YSE2BgC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 2: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Ty0N969dcssC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 3: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=AQNt4YmhZagC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 4: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=9T_n2tA7l4EC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 5: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=6ILdAgAAQBAJ&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s

This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
 Tuesday, June 5, 2018 at 2:18PM
Tuesday, June 5, 2018 at 2:18PM 
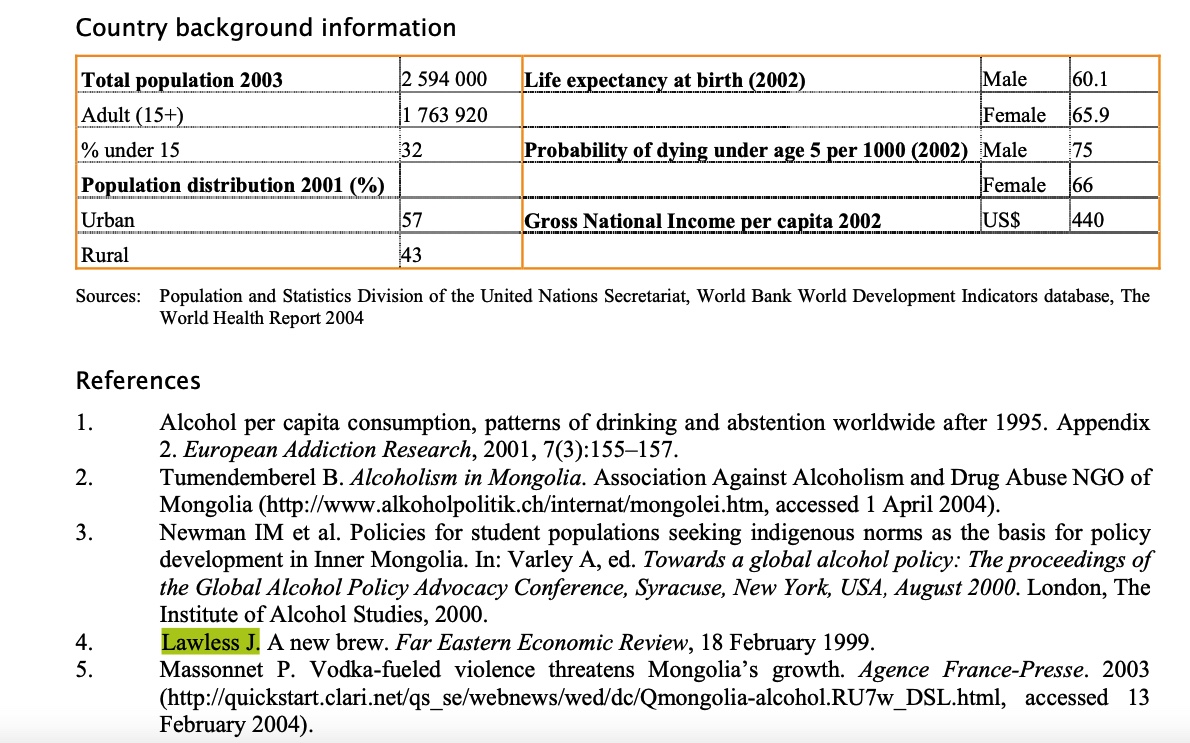 Jill's story for the Far Eastern Economic Review is cited in the WHO Global Status Report on Alcohol 2004.
Jill's story for the Far Eastern Economic Review is cited in the WHO Global Status Report on Alcohol 2004.  Wild East: Travels in the New Mongolia by Jill Lawless offers a vibrant account of what it was like to be a journalist in Mongolia in the late 1990s.
Wild East: Travels in the New Mongolia by Jill Lawless offers a vibrant account of what it was like to be a journalist in Mongolia in the late 1990s.  David South,
David South,  David South Consulting,
David South Consulting,  Ger,
Ger,  Jill Lawless,
Jill Lawless,  UN,
UN,  colour,
colour,  digital,
digital,  internet,
internet,  magazine,
magazine,  media,
media,  newspapers,
newspapers,  online in
online in  Austerity,
Austerity,  Cities,
Cities,  David South Consulting,
David South Consulting,  Digital,
Digital,  Media,
Media,  Shock Therapy,
Shock Therapy,  UB Post,
UB Post,  UNDP,
UNDP,  UNDP Mongolia,
UNDP Mongolia,  Youth
Youth