
A clever innovator from India has built a highly durable solar lantern that also doubles as a mobile phone charger.
The Sunlite lantern – the JS 30 MOB Sunlite – made by Sunlite Solar (sunlite-solar.com) is an LED (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Light-emitting_diode) light packed with clever innovations. It is completely self-contained and does not require any extra parts, cables or separate solar panel to charge it. The clever design includes a pop-up, fold-down handle, a powerful solar PV (photovoltaic) panel on its top that – with a day out in the sun – charges the lantern’s battery enough to provide around 8 hours of 360-degree light when the sun goes down. It is also highly durable and moisture and heat resistant and can withstand a drop on a hard floor.
The manufacturer of the Sunlite lantern is India Impex, which focuses on making and exporting high quality off-grid solar lighting products and sees itself as a “socially driven company.” Founded in 2009, it has built up its reputation as a global vendor to humanitarian and relief agencies.
To date, the Sunlite lantern has been distributed to people following Japan’s 2011 earthquake and tsunami, after Thailand’s 2011 floods and to refugees caught up in the ongoing crisis in Syria.
“For the size of the lamp, for the number of hours, for the features we give, including the mobile (phone) charging – we are 100 per cent portable – it is all integrated,” said Sunlite representative Divyesh Thakkar, while demonstrating the lantern at the 2012 Global South-South Development Expo, held recently in Vienna, Austria (southsouthexpo.org).
The mobile phone charging capability has been seized as a great way to turn the lantern into an income-generating opportunity. Already, people are forming co-ops and charging rent time on the lantern for recharging mobile phones. And there are a few clever tweaks to the lantern to help control this.
“I don’t want this to be abused – I want it to be smart,” said Thakkar. “When someone comes in and charges the mobile phone and forgets, it is going to cut off after 20 minutes.”
Sunlite lanterns have many uses, according to the product’s maker. One aspect the manufacturer is emphasizing is the importance of light to the security of women and children. There is overwhelming evidence that better lighting makes for a more secure environment, and allows people to do more things safely at night. Children can look out for environmental threats such as poisonous snakes and spiders, and women and girls can feel safe doing things like going to the toilet without worrying that somebody might attack them in the dark.
Solar power is being seen as a way to get electricity to people in areas bypassed by conventional electricity grid networks. It also helps move people away from expensive, polluting and dangerous alternatives such as diesel generators, paraffin lamps, gas stoves and coal or dung fires.
“We compare our solar lantern to the kerosene lantern,” Sunlite representative Sagar Mehta explained. “On a payback basis, you use an approximate of 30 to 40 cents of a US dollar of kerosene every day for a four-hour light. First of all, it is very harmful – smoke inhalation, illnesses, burns, all sorts of things, security issues.
“That will cost a family one third or half of its income on a daily basis. If we can change this around where if we can make a solar lantern, where the sun is free, that can pay back in three months and you start earning rather than paying, (they are) making a living.”
Solar-powered devices have many advantages. They can power up their batteries during the day while sitting in the sunshine and then be a source of light and electricity at night. This free energy source reduces the cost of running lights at night and means people can do a wide range of activities, from reading and studying to running a business or socializing. Some have even used Sunlite lanterns as landing lights for aircraft runways in Africa.
Sunlite lanterns are currently being distributed to people in disaster situations and also in refugee camps and displaced persons communities.
“The lamp was developed as a basic light for refugees who don’t have anything and have been displaced from homes,” said Mehta. “We supply in excess of 50,000 lamps every year to aid agencies, in particular the (UN’s) refugee agency.”
In order to keep tight control on quality and be able to have an inventory of lanterns ready to go on a moment’s notice, the company has invested in and set up its own in-house manufacturing facilities in India.
Sunlite Solar sees itself as a social enterprise. It is not focused on quick profits, and developing the lantern has taken time.
“It requires a huge amount of investment and time,” said Thakkar. “We spent two years without selling a single piece. What we did was our R&D and went out in the field, some of the most dangerous places – Rwanda, Uganda – actually training people to use it and getting the awareness.
“When you work with the UN, when you work through other government channels, it is just a long process which you have to be willing to go through.”
By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions
Published: December 2012
Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP's South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South's innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.
Follow @SouthSouth1
Google Books: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=q1KeBgAAQBAJ&dq=development+challenges+december+2012&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Slideshare: http://www.slideshare.net/DavidSouth1/development-challengessouthsouthsolutionsdecember2012issue
Southern Innovator Issue 1: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Q1O54YSE2BgC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 2: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Ty0N969dcssC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 3: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=AQNt4YmhZagC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 4: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=9T_n2tA7l4EC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 5: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=6ILdAgAAQBAJ&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s

This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
 Monday, November 6, 2017 at 11:25AM
Monday, November 6, 2017 at 11:25AM 
 Eco-cities Up Close in Southern Innovator Issue 4.
Eco-cities Up Close in Southern Innovator Issue 4.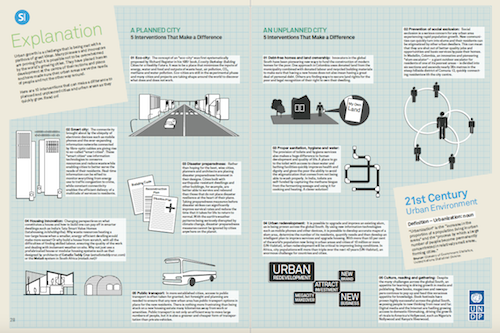 An infographic showing planned and unplanned cities.
An infographic showing planned and unplanned cities.  Southern Innovator Issue 4: Cities and Urbanization is published by the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC).
Southern Innovator Issue 4: Cities and Urbanization is published by the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC). The first five issues of Southern Innovator. The highly influential magazine was distributed around the world and each issue was launched at the annual Global South-South Development (GSSD) Expo hosted by the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC).
The first five issues of Southern Innovator. The highly influential magazine was distributed around the world and each issue was launched at the annual Global South-South Development (GSSD) Expo hosted by the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC).




