
The Caribbean nation of Haiti is the poorest country in the western hemisphere, with 80 percent of the population living below the poverty line (CIA World Factbook). The country had been enjoying some positive economic growth since 2005 after decades of economic and political turmoil.
The country’s political vacuum and economic problems gave rise to violent gang rule on its streets and a collapse in public services, in particular garbage collection. The piles of waste became a source of disease and squalor as well as providing barricades for gangs to wage their street battles.
Haiti was also hit by four devastating hurricanes in 2008, with heavy damage to the country’s agricultural sector and transport infrastructure.
But a project by UNDP’s Special Unit for South-South Cooperation (http://ssc.undp.org/Home.118.0.html) has turned around a Haitian neighbourhood by simultaneously cleaning up the garbage, creating employment and income and reducing gang violence and despair. The United Nations has been working in Haiti to restore the economy and bring peace and good government to the country since the 1990s. Its most recent mission, MINUSTAH (http://minustah.org/), has been running since 2004.
Called ‘Love n’ Haiti’ and located in the Carrefour-Feuilles district (http://www.maplandia.com/haiti/ouest/carrefour-feuilles/) of the capital Port-au-Prince, the project used a ground-up strategy to tackle the problem of waste removal.
“I know we have a bad image. But the violence is going down in my neighbourhood,” said Gislène La Salle, a widow and a mother of six from Carrefour-Feuilles, to the Indo-Asian News Service (IANS).
“But when the security situation deteriorated sharply, I could not work in the streets. Luckily, six months ago, I found work in this project. Now, life is more stable. I have a regular income,” she said.
“The money I earn allows me to feed my family better and send three of my six children to school.”
The neighbourhood has a population of 150,000. Nine community leaders were identified and a management committee set up called the Committee d’Action Sanitaire de Carrefour Feuilles (CASCAF). The management committee then undertook difficult negotiations with local street vendors to establish garbage collection points. A waste collection plan was drawn up, and around 400 workers were hired to clean the streets and canals and collect the waste.
The workers were divided up into nine street cleaning teams and three waste collection teams, comprising people who were members of rival groups.
The project started in 2006 from a very basic point: generating awareness in the population about the dangers of waste and the need for it to be disposed of. The breakdown in public services from decades of political turmoil and poverty had meant a culture of waste disposal no longer existed. The project drew on similar experiences in Brazil and used Brazilian expertise.
A triage (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Business_Triage) centre was set up to sort the waste into paper, plastic, metal, glass and organic matter for recycling. Two products are made from the waste to earn income: cooking briquettes and fertilizer.
The cooking briquettes may also help stem Haiti’s horrific deforestation. The country shares its island with the Dominican Republic in the Caribbean, and anyone flying over the island can see a sharp dividing line between the green and lush forests of the Dominican Republic and the almost-barren and dusty Haitian hills.
By turning the trash into cooking briquettes, people are being offered an alternative to chopping down the forests and burning trees to make charcoal fuel for cooking.
Income for the waste collectors has increased to US $3 a day and the project has removed 70 percent of the neighbourhood’s waste, making it easier to get around and get things done (another boost to incomes).
Georginette is also a widow. Like Gislène, this mother of seven is thrilled to find a regular job. “Earlier, only three of my seven children went to school. Many children from the neighbourhood roamed the streets. But since November 2007 when I began working here, I can afford to send five,” she said.
Prior to the project, the neighbourhood was one of the most dangerous in Port-au-Prince. The project unexpectedly found the history of violence and conflict were quickly overcome when the project began to make quick progress.
Collecting the waste now earns an income for 380 families. And by gravitating community leadership to nonviolent leaders, relationships between people and groups improved.
The 50 waste collection points and public garbage bins now contribute to a reduction in common diseases that are rife in other parts of Haiti: leptospirosis, worms, canicola fever, tetanus, yellow fever, typhoid, dengue, and malaria.
Originally, the government of Haiti appealed to the India, Brazil and South Africa Facility for Poverty and Hunger Alleviation (IBSA Trust Fund) (http://www.indianembassy.org/newsite/press_release/2007/Sept/17.asp) to get to grips with the woeful garbage collection in the capital, while tackling the violence in the slums and lack of economic opportunity.
The project is also a partnership between Port-au-Prince’s city hall, the Ministry of Public Works and other government ministries, Quisqueya University, UNDP Haiti, IBSA, and the Special Unit for South-South Cooperation. The project is run on the ground by UNDP Haiti.
Where once the trash made flooding worse by blocking canals, having it removed has prevented the stew of waste that was produced when floods occurred.
“Impressed by the positive results so far, the Haitian government would like to replicate this model in other regions of the country,” said Eliana Nicolini, the UNDP project coordinator.
It is hoped the project can be scaled up to reach across Haiti and even be replicated in other countries. The UN Special Envoy for Haiti, former US President Bill Clinton, has been drafted in to help with raising funds for expanding the project.
The Love n’ Haiti project has been selected by the BBC’s World Challenge contest, which invites the general public to vote for which project they think is the best. Voting takes place on their website:http://www.theworldchallenge.co.uk. The project is number eight in the list on the website.
“It is not easy to choose who to hire in a place where so many are desperately in need of work. Many people beg us for work but we don’t have vacancies at the moment. If we can hire even 100 more persons, it would solve a lot of problems,” said Patrick Massenat, a local youth heading a committee created to implement activities contributing to waste management and to ensure effective involvement of governmental institutions.
“Most people in this area never knew real work. Now, they have experienced it. They also have families. The area is cleaner; the women who lost their husbands in gang wars and police firing are happier. It’s a beginning.”
By David South, Development Challenges, South-South Solutions
Published: October 2009
Development Challenges, South-South Solutions was launched as an e-newsletter in 2006 by UNDP's South-South Cooperation Unit (now the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation) based in New York, USA. It led on profiling the rise of the global South as an economic powerhouse and was one of the first regular publications to champion the global South's innovators, entrepreneurs, and pioneers. It tracked the key trends that are now so profoundly reshaping how development is seen and done. This includes the rapid take-up of mobile phones and information technology in the global South (as profiled in the first issue of magazine Southern Innovator), the move to becoming a majority urban world, a growing global innovator culture, and the plethora of solutions being developed in the global South to tackle its problems and improve living conditions and boost human development. The success of the e-newsletter led to the launch of the magazine Southern Innovator.
Follow @SouthSouth1
Google Books: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=tRKYBgAAQBAJ&dq=development+challenges+october+2009&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Slideshare: http://www.slideshare.net/DavidSouth1/development-challengessouthsouthsolutionsoctober2009issue
Southern Innovator Issue 1: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Q1O54YSE2BgC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 2: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=Ty0N969dcssC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 3: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=AQNt4YmhZagC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 4: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=9T_n2tA7l4EC&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s
Southern Innovator Issue 5: https://books.google.co.uk/books?id=6ILdAgAAQBAJ&dq=southern+innovator&source=gbs_navlinks_s

This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 3.0 License.
 Monday, November 6, 2017 at 11:25AM
Monday, November 6, 2017 at 11:25AM 
 Eco-cities Up Close in Southern Innovator Issue 4.
Eco-cities Up Close in Southern Innovator Issue 4.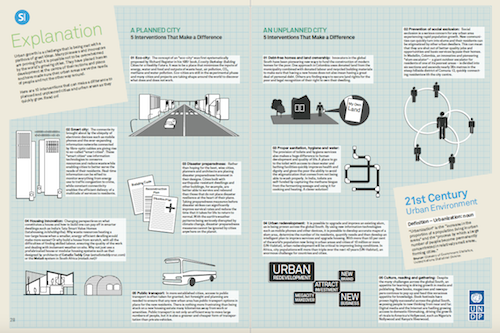 An infographic showing planned and unplanned cities.
An infographic showing planned and unplanned cities.  Southern Innovator Issue 4: Cities and Urbanization is published by the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC).
Southern Innovator Issue 4: Cities and Urbanization is published by the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC). The first five issues of Southern Innovator. The highly influential magazine was distributed around the world and each issue was launched at the annual Global South-South Development (GSSD) Expo hosted by the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC).
The first five issues of Southern Innovator. The highly influential magazine was distributed around the world and each issue was launched at the annual Global South-South Development (GSSD) Expo hosted by the United Nations Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC).



